Zinc (Zn) is an essential micronutrient for plant life. In Minnesota, while some soils are capable of supplying adequate amounts for crop production, addition of zinc fertilizers is needed for others. Zinc is a recommended micronutrient in fertilizer programs for production of corn, sweet corn, and edible beans. Several research projects have focused on the use of this nutrient, and much of the following information is based on the results of that research.
Natural sources of zinc
Zinc exits naturally in rocks. The amount of zinc present in the soil depends on the parent materials of that soil. Sandy and highly leached acid soils generally have low plant available zinc. Mineral soils with low soil organic matter also exhibit zinc deficiency. In contrast, soils originating from igneous rocks are higher in zinc. Plants take up zinc as the divalent ionic form (Zn2+) and chelated-zinc.
The role of zinc in the plant
Zinc is an important component of various enzymes that are responsible for driving many metabolic reactions in all crops. Growth and development would stop if specific enzymes were not present in plant tissue. Carbohydrate, protein, and chlorophyll formation is significantly reduced in zinc-deficient plants. Therefore, a constant and continuous supply of zinc is needed for optimum growth and maximum yield.
Zinc deficiency
Research at the University of Minnesota as well as other universities has identified soil conditions where a response to zinc fertilizers is expected. These conditions are:
Soil Temperature: Cool soil temperatures in early spring can intensify the need for zinc. When soil temperature is low, mineralization of soil organic matter slows down resulting less amount of zinc being released in the soil solution. Root growth is also stunted by cool temperatures and reduces the plant’s ability to find new sources of zinc in the soil profile.
- Soil Texture: In Minnesota, crop response to fertilizer-zinc takes place mostly on fine-textured soils. Recent studies indicate a response to zinc can occur when high yielding crops are grown on sandy soils with low organic matter content. However, the measured response to zinc fertilization in these situations has been small and has not occurred every year. Soil tests for zinc are recommended to determine if zinc is needed in a fertilizer program.
- Topsoil Removal: The probability of a response to zinc fertilization increases where topsoil has been removed or eroded away. When soils are eroded, the amount of free calcium carbonate on the soil surface increases. The need for zinc in a fertilizer program increases as the percentage of free calcium carbonate increases.
- Previous Crop: The probability of a response to zinc fertilization increases if either corn or dry edible beans follows a crop of sugar beets (a non-mycorrhizal plant). This condition is termed as “fallow syndrome” and is a result of poor colonization of the plant root with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus which increases the plant’s ability to take up phosphorus and zinc.
- Phosphorus Level: There is a known relationship between phosphorus and zinc in the soil. Previous studies in Minnesota have shown excessive application of phosphate fertilizers caused zinc deficiency in corn, which resulted in reduced grain yield. This yield reduction occurred mainly in calcareous soil with high pH (pH > 8.3) and low soil test phosphorus and zinc. A phosphorus-induced zinc deficiency is a concern and may occur only if very high rates of phosphate fertilizer (more than 200 lb P2O5/acre) are used and the soil test for zinc is in the range between Low and Very Low.
Crops that respond to zinc
Crops vary in Zn required to complete their life cycle. Table 1 shows the response to Zn that might be expected from various crops.
Table 1. Potential for a crop response to zinc when applied to zinc deficient soils.
| Large response to Zn | Moderate response to Zn | Small response to Zn |
|---|---|---|
| Apple, dry edible beans, corn, onion, snap bean, sweet corn | Grape, lettuce, potato, soybean, tomato | Alfalfa, asparagus, barley, canola, carrot, clovers, grass pasture, oat, peas, rye, sugar beet, sunflower, wheat |
Deficiency symptoms
Plants fail to develop normally when they are deficient in zinc and certain characteristic deficiency symptoms will appear. With corn, these symptoms usually appear in the first two or three weeks of the growing season. If the deficiency of zinc is severe, these symptoms may last throughout the entire season.
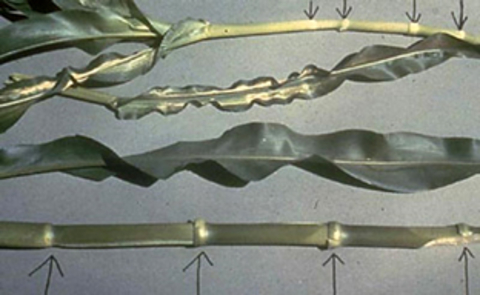
A deficiency of zinc in corn is characterized by the development of broad bands of striped tissue on each side of the midrib of the leaf (Figure 1). These stripes begin on the part of the leaf closest to the stalk and appear first on the upper part of the plant. A zinc-deficient corn plant also appears to be stunted. The lack of normal elongation in a corn plant is shown in Figure 2.
Zinc deficiency in edible beans first appears as a yellowing of the lower leaves. As the season progresses, this yellowing develops into a bronze or brown color. The leaves have a rusty appearance. For this crop, however, care must be taken to avoid confusing sunburned leaves with zinc deficiency.
Zinc deficiency in soybean is not common in Minnesota. Symptoms of zinc deficiency in soybean include interveinal mottling or chlorosis (Figure 3) similar to symptoms in dry edible beans. Zinc deficiency should not be confused with iron deficiency chlorosis which is more common in soybean in Minnesota.
For both corn and edible beans, suspected zinc deficiency symptoms should be confirmed with plant tissue analysis.
Phosphorus-induced zinc deficiency might be a concern when high rates of manure are applied to crop land. The manure, however, also contains zinc that can be used for crop growth. Therefore, phosphorus supplied from manure should not create a zinc deficiency for crop production in Minnesota.
Predicting the need for tissue and soil tests for zinc
The need for zinc in a fertilizer program can be determined through soil tests and plant analyses. Plant analyses can confirm a suspected zinc deficiency during the growing season. However, plant analysis should be used in combination with soil tests before arriving at firm recommendations for using zinc in a fertilizer program.
A guide to sufficient levels of zinc in the tissue of several important agronomic and horticultural crops grown in Minnesota is provided in Table 2. Tissue zinc concentration varies between growth stages. It is important that crops be sampled at the growth stage listed if interpretation of plant analysis information is to be accurate.
Table 2. Sufficiency levels of zinc for major agronomic crops, vegetables, and fruits grown in Minnesota
| Crop | Plant part | Time | Sufficiency range (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alfalfa | Tops (6" new growth) | Prior to flowering | 21-70 |
| Apple | Leaf from middle of current terminal shoot | July 15-August 15 | 20-50 |
| Blueberry | Young mature leaf | First week of harvest | 25-60 |
| Broccoli | Young mature leaf | Heading | 20-80 |
| Cabbage | Half-grown young wrapper leaf | Heads | 20-200 |
| Carrot | Young mature leaf | Mid-growth | 25-250 |
| Cauliflower | Young mature leaf | Buttoning | 20-250 |
| Edible bean | Most recently matured trifoliate | Bloom stage | 15-80 |
| Field corn | Whole tops | Less than 12" tall | 20-70 |
| Base of ear | Initial silk | 20-70 | |
| Grape | Petiole from young mature leaf | Flowering | 20-45 |
| Pea | Recently matured leaflet | First bloom | 25-100 |
| Potato | Fourth leaf from tip | 40-50 days after emergence | 20-40 |
| Petiole from fourth leaf to tip | 40-50 days after emergence | 20-40 | |
| Raspberry | Leaf 18" from tip | First week in August | 15-60 |
| Soybean | Trifoliate leaves | Early flowering | 21-80 |
| Spring wheat | Whole tops | As head emerges from boot | 15-70 |
| Strawberry | Young mature leaf | Mid-August | 20-50 |
| Sweet corn | Ear leaf | Tasseling to silk | 20-100 |
| Sugar beet | Recently matured leaves | 50-80 days after planting | 10-80 |
When a soil test indicates the need for zinc, small amounts are needed in a fertilizer program to provide for optimum yield. The zinc status of Minnesota soils can be easily measured by routine soil tests. The DTPA procedure is used by majority of soil testing laboratories and is a reliable indicator of the need for zinc in a fertilizer program. The interpretations of this test, along with corresponding fertilizer recommendations, are summarized in Table 3.
Table 3. Zinc recommendations for field corn, sweet corn, and edible beans grown in Minnesota
| Soil test zinc* | Zinc to apply (lbs/ac) | Zinc to apply (lbs/ac) |
|---|---|---|
| ppm | Broadcast | Band |
| 0.0-0.25 | 10 | 2 |
| 0.26-0.50 | 10 | 2 |
| 0.5-0.75 | 5 | 1 |
| 0.76-1.00 | 0 | 0 |
| 1.01+ | 0 | 0 |
Table 4. Effect of zinc rates on corn grain yield at four locations near Red River Valley, Minnesota. Zinc rates applied as broadcast zinc sulfate (36% zinc)
| County | ST Zn* | Zinc rate (lb/ac)** | Zinc rate (lb/ac)** | Zinc rate (lb/ac)** | Zinc rate (lb/ac)** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ppm | 0 bu/ac | 5 bu/ac | 10 bu/ac | 15 bu/ac | |
| Polk | 1.36 | 171a | 164a | 169a | 167a |
| Mahnomen | 0.37 | 168b | 169b | 179a | 191a |
| Red Lake | 0.65 | 211a | 199a | 195a | 194a |
| Marshall | 0.55 | 134a | 132a | 143a | 135a |
Table 5. Corn grain yield for plots with (+zinc) and without (-zinc) 1 quart/acre of a 10% fully chelated zinc with 10-34-0
| Location | ST Zn* | Corn Grain yield (bu/ac) | Corn Grain yield (bu/ac) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ppm | - zinc | + zinc | |
| Murdock | 2.8 | 192 | 192 |
| Waseca | 1.4 | 189 | 200 |
| St. Charles | 1.7 | 198 | 197 |
| Willmar | 1.0 | 173 | 172 |
| Prinsburg | 2.6 | 209 | 204 |
| Stewart | 1.3 | 167 | 162 |
| Becker | 1.1 | 192 | 184 |
| Lamberton | 0.6 | 213 | 212 |
Zinc Experiments in Minnesota
Corn
Corn is the most widely grown crop in Minnesota where a zinc deficiency is more likely. Soil test zinc should be a primary consideration when deciding to apply zinc for corn. Application of zinc can be highly profitable on soils that test low in zinc (Table 4). If broadcast applied, any zinc not utilized by the crop may be used in following years and will be picked up in soil tests taken following application.
A common practice in Minnesota is to include a chelated zinc source with liquid fertilizer applied directly on the corn seed with the planter at a rate of 1 quart per acre. Application of zinc in the band on the corn seed does not increase the chance of a grain yield response from the application of starter for corn. Several research trials were conducted across Minnesota including 1 quart of a 10% fully chelated source of zinc (Table 5). One of the eight sites in the study fell below 0.75 ppm extractable zinc, but corn grain yield did not significantly increase with in-furrow zinc application. A profitable response when in-furrow zinc is used is still more likely when soils test less than 0.75 ppm (DTPA zinc test).
Soybean
There has been no documented evidence of an increase in soybean grain yield from the application of zinc. A total of 31 locations were studied from 2011 to 2014 in an area ranging from northwest to southeast Minnesota. The DTPA soil test zinc concentration ranging from 0.4 to 3.9 ppm. Soybean grain yield was not increased by Zn at any location. Soil test values suggested for responsive crops such as corn and edible beans should not be used for crops that are not highly susceptible to a zinc deficiency.
Table 6. Soybean grain yield data collected from several studies across Minnesota during 2011-2014 growing seasons. The plots were treated with (+zinc) 10 lb/acre and without (-zinc) zinc fertilizers.
| Year | Location | St Zn (ppm)* | Grain yield (bu/acre) | Grain yield (bu/acre) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - zinc | + zinc | |||
| 2011 | Kittson | 0.8 | 64.6 | 64.4 |
| Redwood | 0.8 | 46.2 | 45.2 | |
| Olmsted | 3.9 | 54.1 | 50.6 | |
| Lake of the Woods | 1.0 | 32.3 | 33.5 | |
| Waseca | 0.9 | 53.2 | 51.7 | |
| Polk | 1.1 | 70.0 | 70.7 | |
| Kitson | 0.8 | 62.1 | 64.8 | |
| Olmsted | 1.9 | 37.4 | 36.8 | |
| Olmsted | 3.9 | 34.1 | 31.5 | |
| 2012 | Polk | 0.6 | 53.2 | 51.7 |
| Kittson | 1.1 | 46.3 | 49.2 | |
| Redwood | 1.0 | 50.3 | 48.6 | |
| Olmsted | 2.1 | 30.5 | 29.5 | |
| Olmsted | 1.6 | 52.4 | 51.4 | |
| Waseca | 0.8 | 42.9 | 44.1 | |
| Norman | 3.2 | 57.7 | 61.1 | |
| Olmsted | 2.3 | 48.1 | 47.6 | |
| Olmsted | 3.9 | 44.3 | 44.7 | |
| Roseau | 0.6 | 44.1 | 45.5 | |
| 2013 | Norman | 0.4 | 28.4 | 25.1 |
| Redwood | 0.9 | 38.2 | 38.0 | |
| Olmsted | 2.1 | 39.5 | 41.4 | |
| Winona | 0.8 | 44.5 | 42.2 | |
| Sibley | 1.5 | 37.1 | 35.3 | |
| Sibley | 1.6 | 40.9 | 40.3 | |
| 2014 | Norman | 1.5 | 37.5 | 38.7 |
| Redwood | 1.9 | 61.3 | 61.3 | |
| Olmsted | 2.8 | 54.0 | 54.2 | |
| Olmsted | 2.5 | 36.5 | 39.7 | |
| Sibley | 1.5 | 45.8 | 44.3 | |
| Sibley | 1.9 | 51.5 | 52.1 |
Fertilizer sources
Several sources can supply zinc when needed. Zinc sulfate (35% zinc) is usually used to supply the needed amount of zinc when dry fertilizer materials are used. This material can be either broadcast and incorporated before planting, or used in a starter fertilizer. It blends well with other dry fertilizer materials. Approximately 3 lb of the zinc sulfate material will supply 1 lb zinc per acre.
A zinc-ammonia complex (10% zinc) can be used to supply zinc when fluid fertilizers are used. This material mixes easily with other fluid fertilizers.
Zinc oxide (78-80% zinc) can correct a zinc deficiency but is slowly soluble and not effective in a granular form. To effectively correct a zinc deficiency, zinc oxide must be finely ground. Spreading any finely ground material is a problem in Minnesota because of the wind. So use of finely ground zinc oxide is limited to situations where suspension fertilizers are used.
Application of poultry manure can add considerable amount of zinc to the soil. For example, broiler litter contains 0.01-0.50 lb zinc/ton and laying hen litter contains an average of 0.15 lb zinc/ton. Because zinc content is variable in manure, it is suggested that manure sources be tested for zinc content before application.
Method of application
The addition of zinc to a starter fertilizer is the most economical approach to zinc fertilization. This method provides the nutrient the year it is needed. This is especially important when corn and edible beans are rotated with other crops. If use of a starter fertilizer is not an option, zinc fertilizers should be broadcast and incorporated before planting of either corn or edible beans.
Foliar applications of zinc have not been consistently effective in correcting deficiencies of this nutrient. This method of application should be used on a trial basis only. For foliar applications, powdered zinc sulfate can be dissolved in water and applied to the leaf tissue. The amount dissolved should supply 0.5 to 1.0 lb zinc per acre when a rate of 20 gallons of water per acre is used.
A zinc chelate can also be mixed with water. The amount of chelate mixed with water should supply 0.15 lb zinc per acre when water is sprayed at a rate of 20 gallons per acre.
Research has shown that all sources of zinc (except granular zinc oxide) have an equal effect on crop production. Consider cost before choosing a source of zinc for the fertilizer program.
Zinc toxicity
Most crops are tolerant to high zinc levels in their tissue without any visible symptoms. Cereals are sensitive to zinc toxicity. Typical toxicity symptoms are iron chlorosis and lack of green color in the leaves.
Summary
- The potential for a response to zinc by crops has not changed in spite of increased zinc removal from high yield crops.
- Crops vary in the potential for a response to zinc when fertilizer is applied to soils with a marginal zinc soil test.
- A response to zinc is possible when the soil DTPA Zn soil test is 0.75 or less and is likely when the DTPA zinc soil test is 0.5 ppm or less.
- Current research does not support the widespread use of chelated zinc applied in-furrow for corn production.
- Banding low rates of zinc may give the greatest economic return for fields that test low in zinc.
Reviewed in 2016