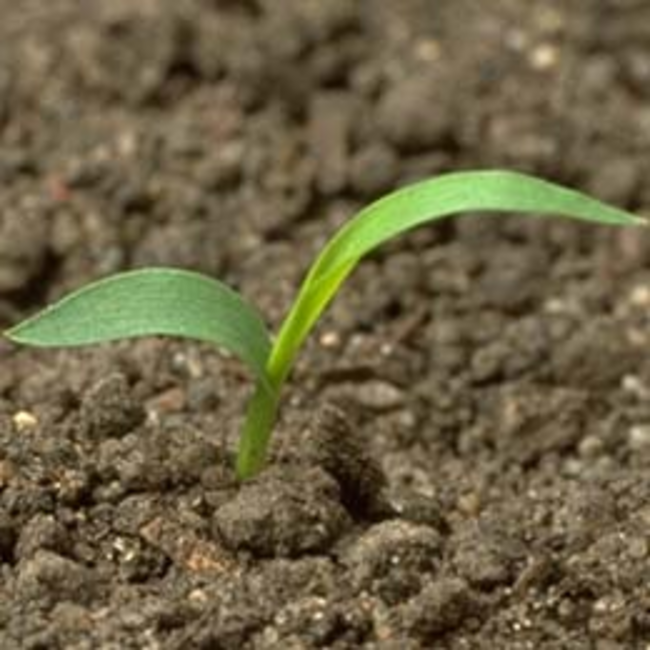
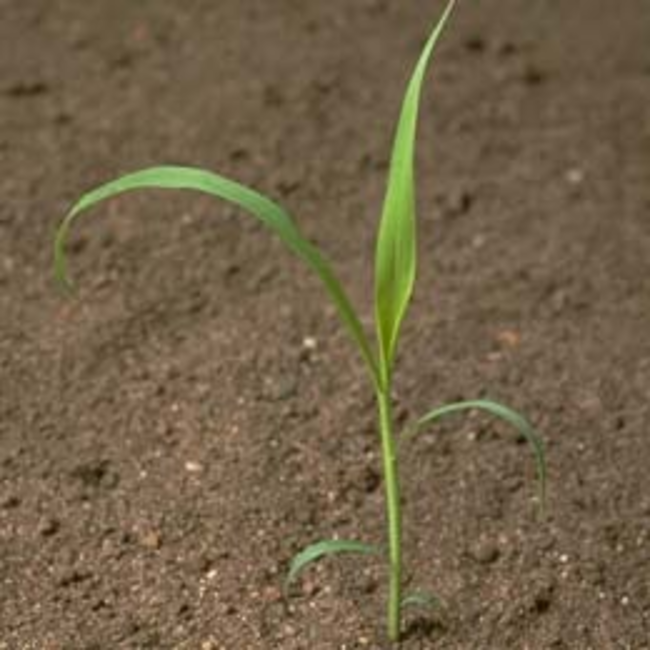
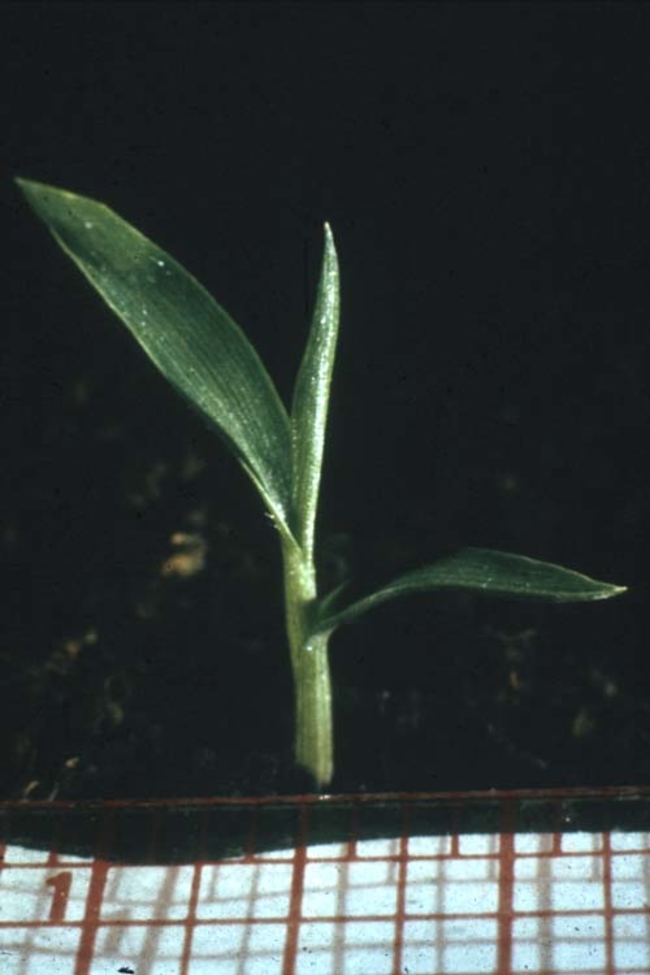
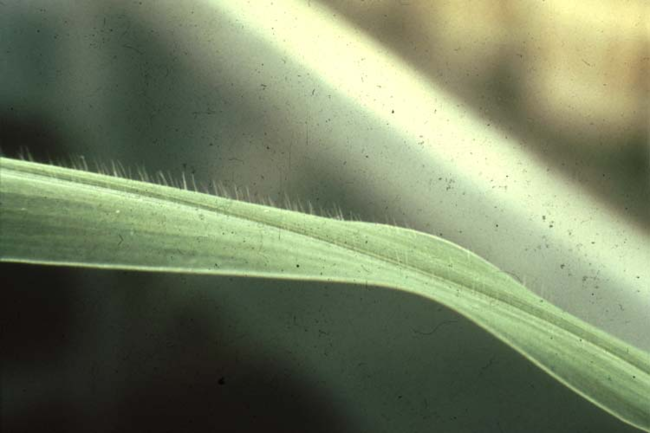
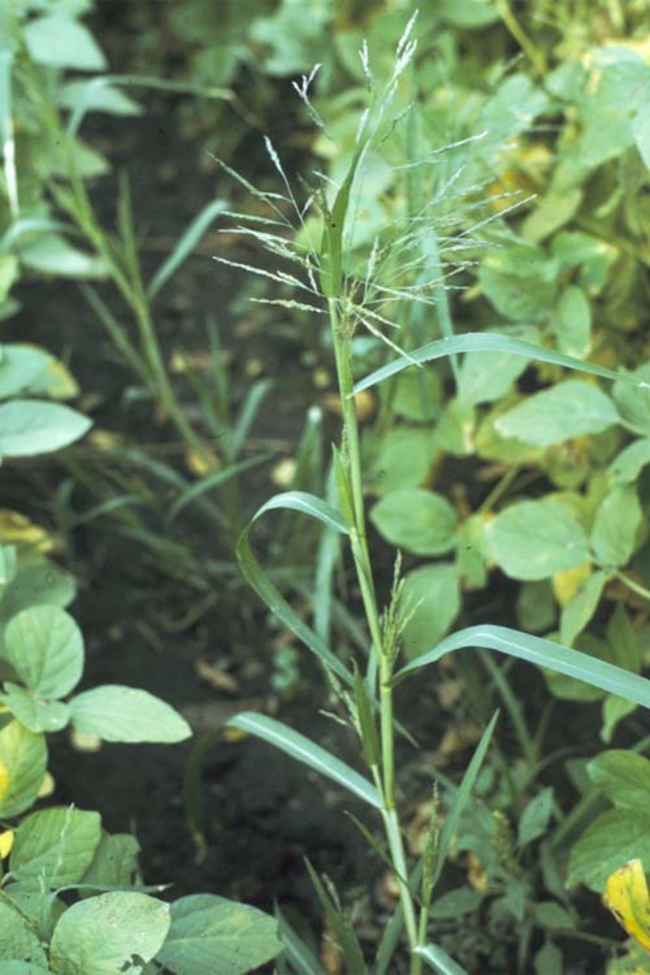
In this guide, you’ll find photos and identifying characteristics of the annual grass weeds common to Minnesota.
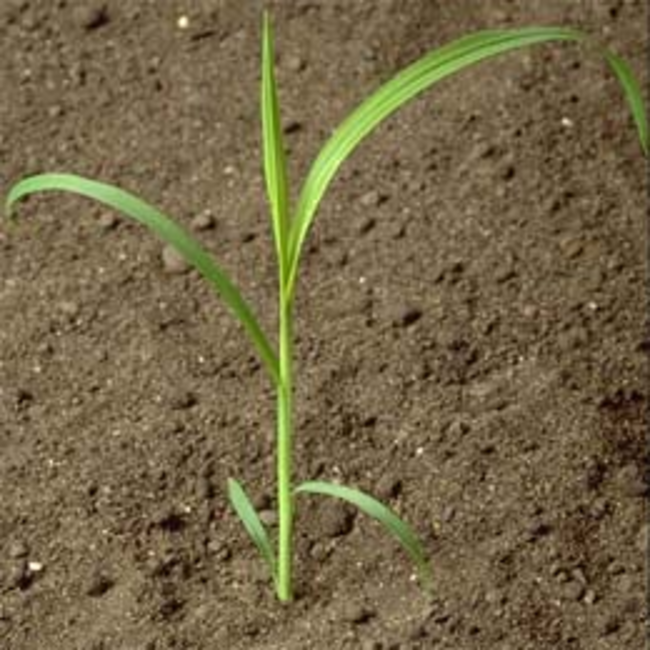
Any or all of these vegetative characteristics may be useful to help identify a young grass weed.
Leaves
-
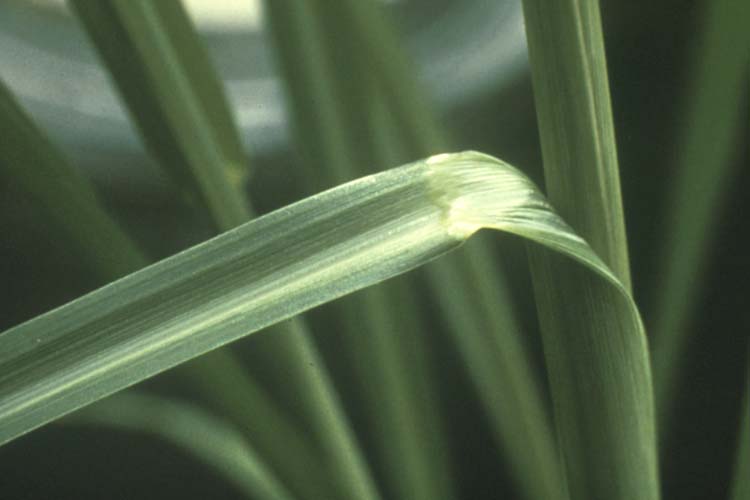
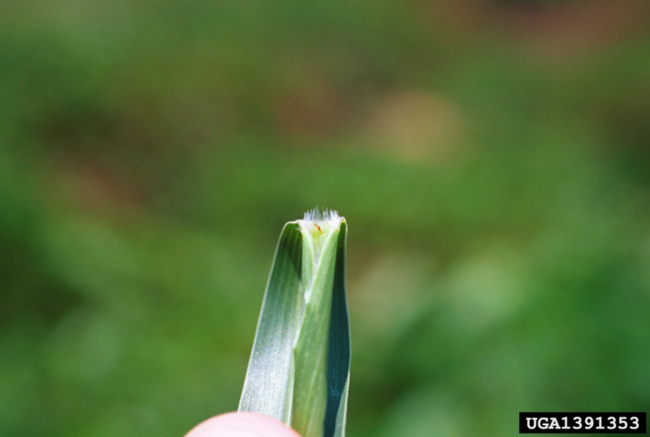
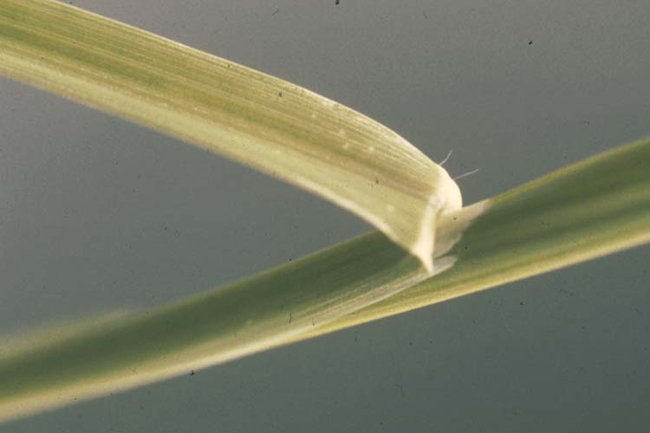
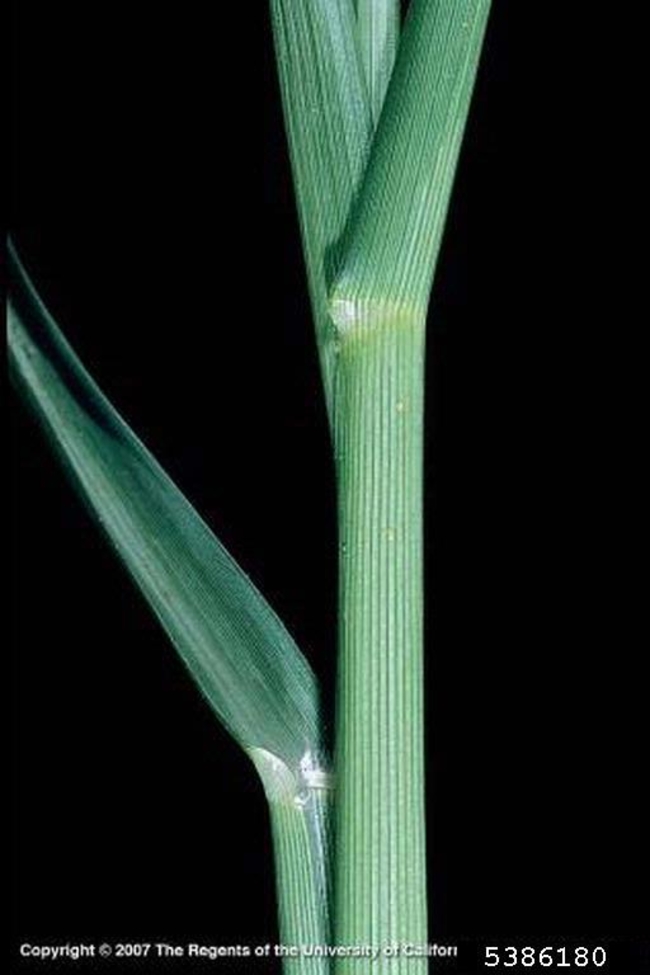
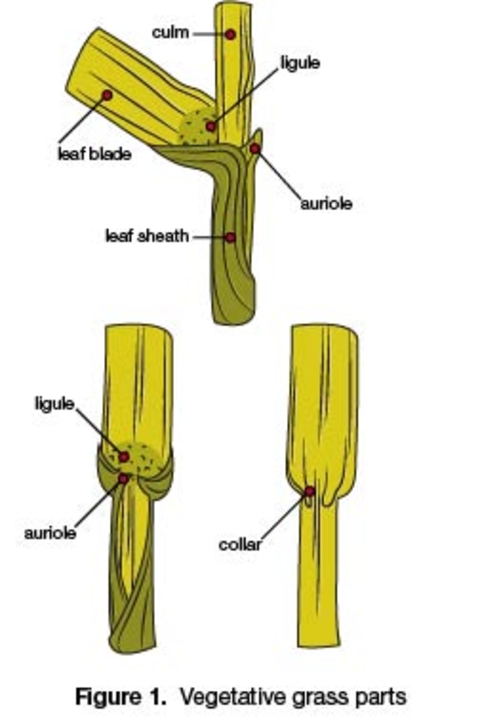
Usually have long, narrow, alternate leaves with parallel venation (distribution or arrangement of veins), with an expanded leaf blade portion and a leaf sheath portion toward the base that encircles the stem (Figure 1).
-
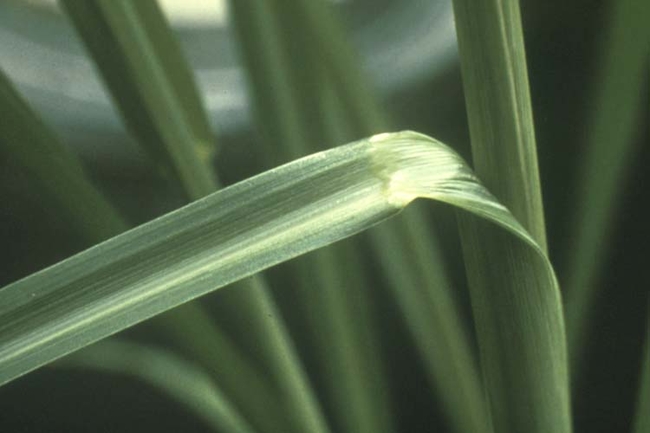
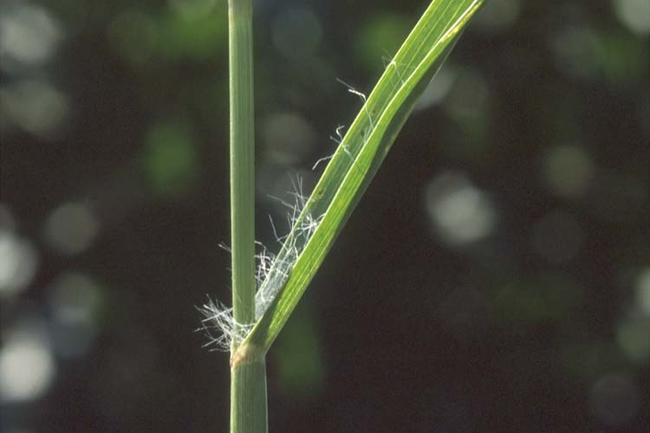
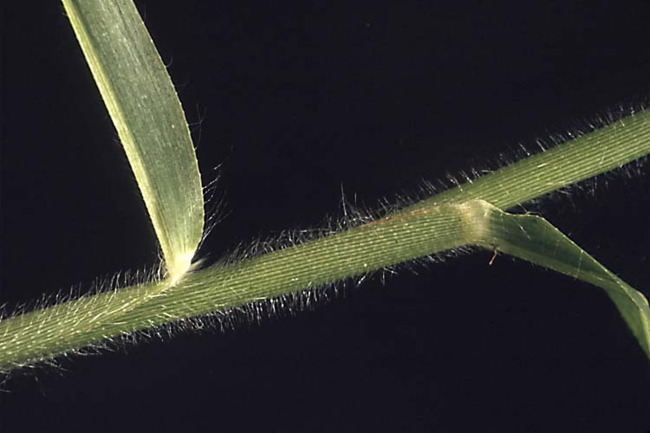
Most have a projection at the base of the leaf blade called a ligule, which may be a membrane, a fringe of hairs or a combination of both.
-
Some have claw-like or hook-like projections at the leaf collar called auricles that may partially encircle the stem. The collar area is the juncture of the leaf blade with the leaf sheath.
-
As grass leaves emerge from the bud shoot, they may be rolled (round) and overlapping, or they may be flat and folded (V-like).
-
Leaf sheaths may be open and overlapping, or they may be closed.
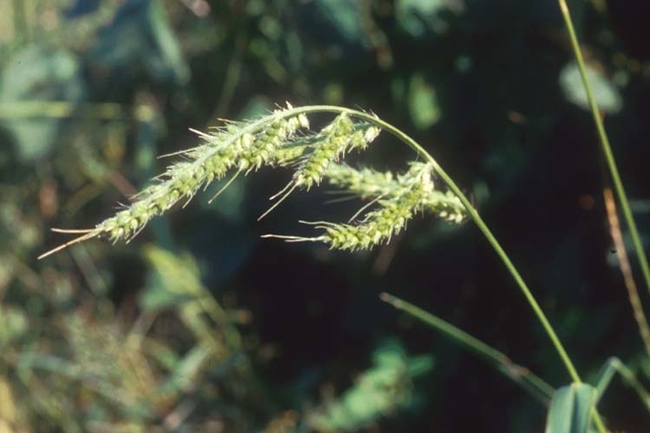
Seeds
-
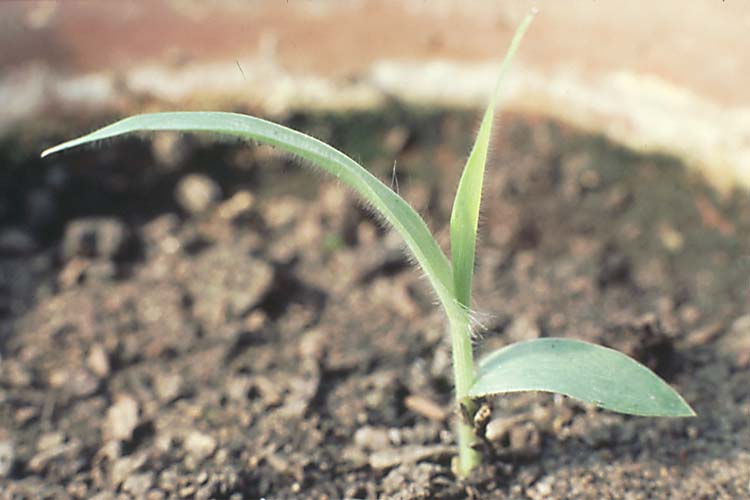
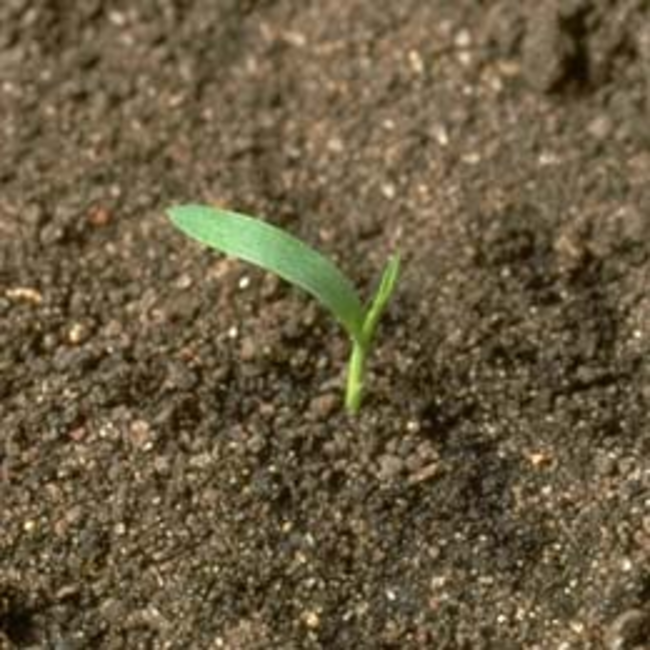
Often remains attached to the primary root after germination. If you carefully remove the grass seedling from the soil, the seed may help identify the plant.
Other plant characteristics
-
Have definite nodes (swollen ridges that encircle the stem) and internodes (portions of the stem area between nodes).
-
Stems (culms) may be round or flattened.
-
May be smooth (glabrous) or hairy.
-
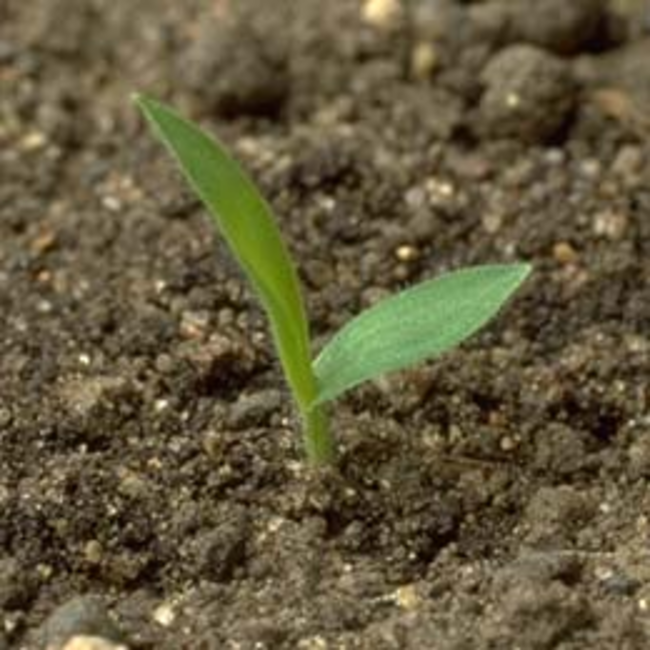
Are monocots, with one cotyledon or seed-leaf that remains in the soil after seed germination.
-
Either annual, with a simple, fibrous root system, or perennial, producing rhizomes, rootstocks or stolons.
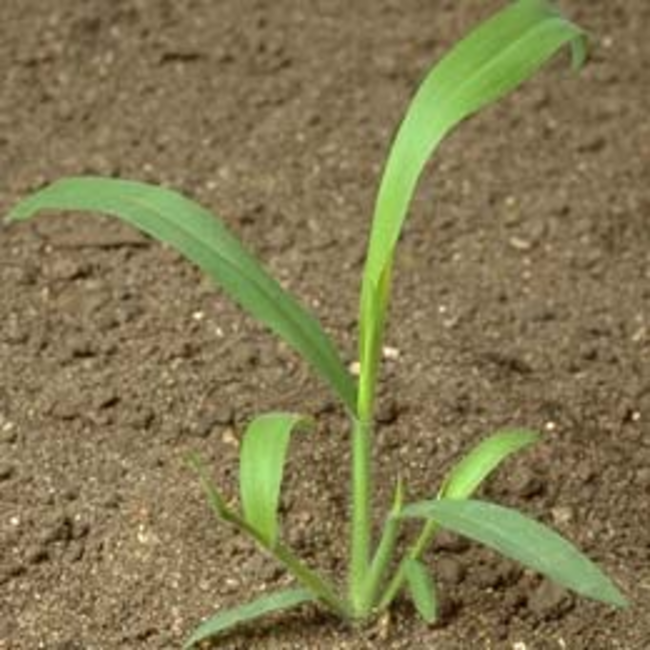
Echinochloa crus-galli (L.) Beauv.
Vegetative characteristics
-
Leaf blade: Smooth and mostly hairless leaf blades. Keeled below.
-
Leaf sheath: Smooth, open, flattened and keeled.
-
Collar: Broad, smooth and yellowish-green. Continuous (not divided by midvein).
-
Ligule: None.
-
Auricles: None
Flowering characteristics
-
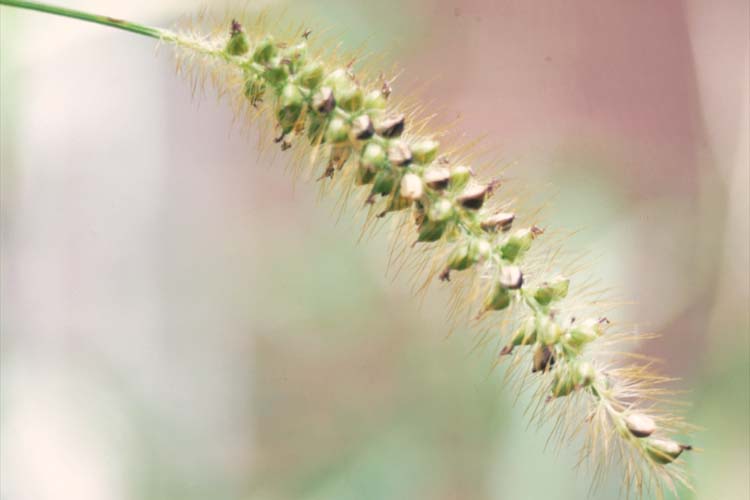
Inflorescence: Raceme-like panicle.
-
Spikelets: Bristly, hairy.
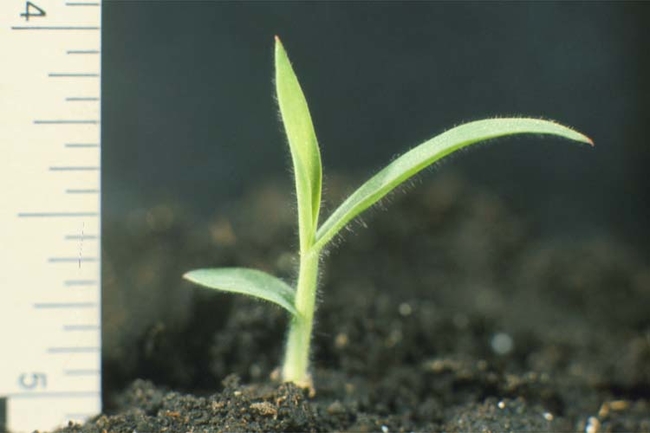
Digitaria sanguinalis
Vegetative characteristics
-
Leaf blade: Densely hairy on both surfaces. Keeled below.
-
Leaf sheath: Open and densely hairy.
-
Collar: Broad and divided by midvein. Hairy on outside edges.
-
Ligule: Membranous and prominent. Rounded to acute with wavy-edged margin.
-
Auricles: None.
Flowering characteristics
-
Inflorescence: Digitate (finger-like) panicle.
-
Spikelets: Pressed closely against panicle.
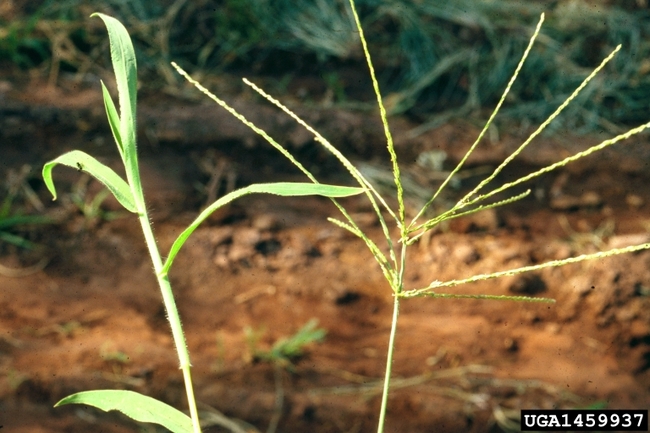
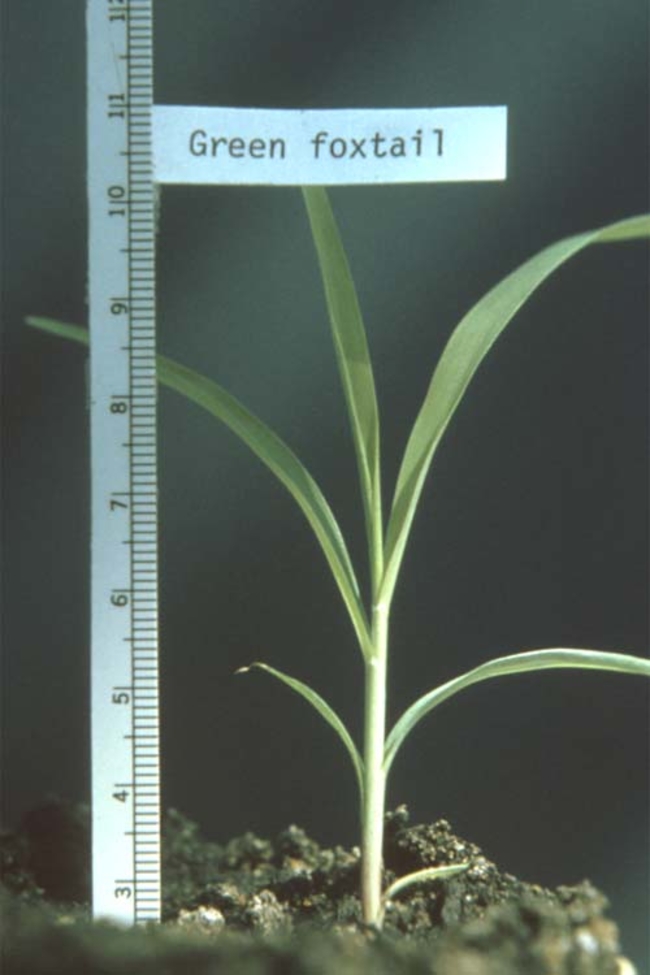
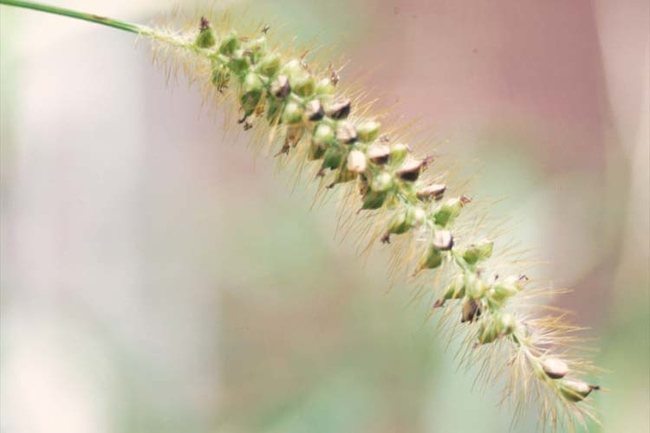
Setaria viridis (L.) Beauv.
Vegetative characteristics
-
Leaf blade: Leaf blades are relatively free of hairs on both upper and lower surfaces.
-
Leaf sheath: Hairy and open, with overlapping margins and stiff, bristle-like hairs on outer margins.
-
Leaf collar: Continuous.
-
Ligule: Fringe of hairs approximately 0.5 millimeters long.
-
Auricles: None
Flowering characteristics
-
Inflorescence: Cylindrical head (compact panicle) about 3 to 4 inches long. Droops or nods from the tip.
-
Spikelets: Crowded, subtended by two to three bristles that arise from the base of the spikelet.
Setaria faberi
Vegetative characteristics
-
Leaf blade: Dense covering of hairs on the leaf blade’s upper surface, and few scattered hairs on the lower surface.
-
Leaf sheath: Hairy, slightly flattened and keeled (ridged at mid-vein). Open with stiff, bristle-like hairs on margins.
-
Collar: Continuous.
-
Ligule: Fringe of hairs 1-2 mm long. Longer hairs at collar margin.
-
Auricles: None
Flowering characteristics
-
Inflorescence: Cylindrical head (compact panicle) about 3 to 5 inches long. Droops from the base.
-
Spikelets: Crowded, subtended by numerous bristles (usually three to six) that arise from the base of the spikelet.
Setaria pumila
Vegetative characteristics
-
Leaf blade: Smooth, except for several prominent whitish hairs near the base on the upper surface.
-
Leaf sheath: Smooth, flattened and sharply keeled.
-
Collar: Smooth and continuous.
-
Ligule: Fringe of hairs.
-
Auricles: None
Flowering characteristics
-
Inflorescence: Short, narrow cylindrical head that’s 2 to 3 inches long (compact panicle).
-
Spikelets: Crowded, subtended by three to six yellow bristles that arise from the base. Seeds are larger than giant or green foxtail.
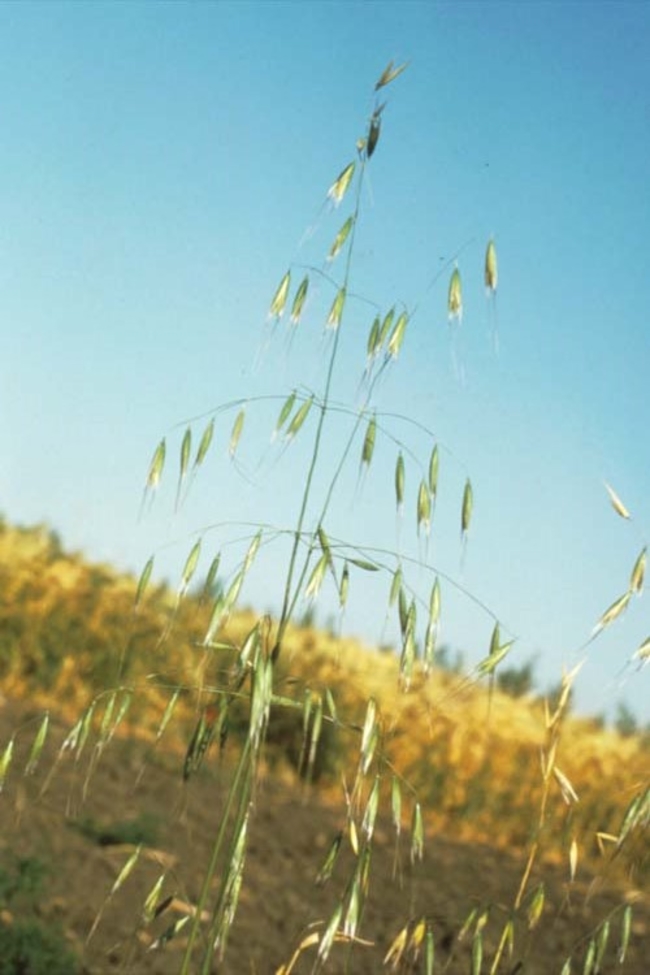
Avena fatua
Vegetative characteristics
-
Leaf blade: Smooth and usually hairless, with the exception of stiff, bristle-like hairs along the lower edge.
-
Leaf sheath: Open, round and often pubescent, with overlapping margins.
-
Collar: Broad and smooth.
-
Ligule: Membranous and prominent.
-
Auricles: None
Flowering characteristics
-
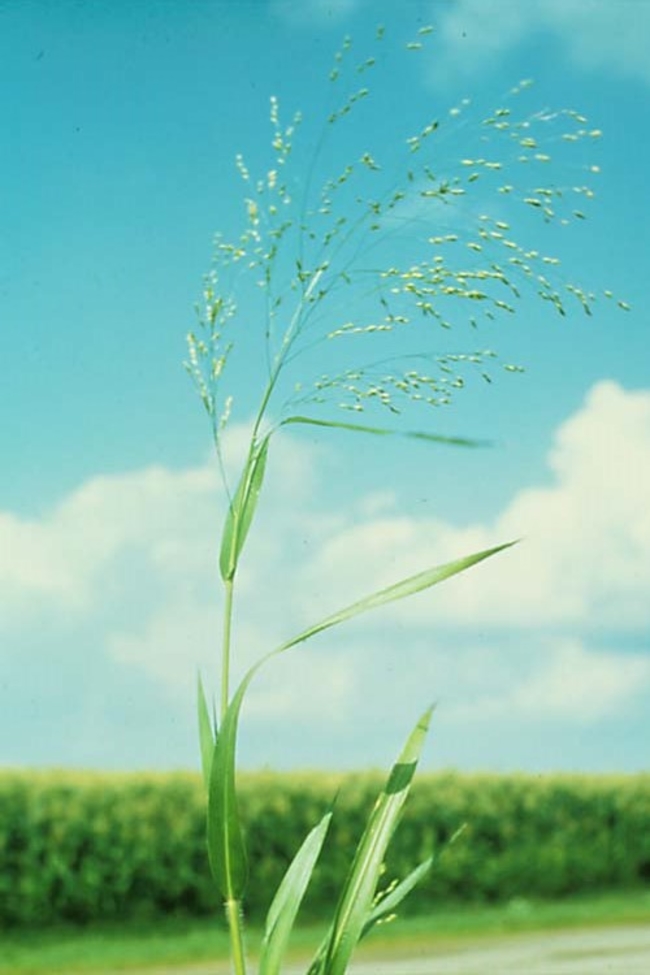
Inflorescence: Spreading, true panicle.
-
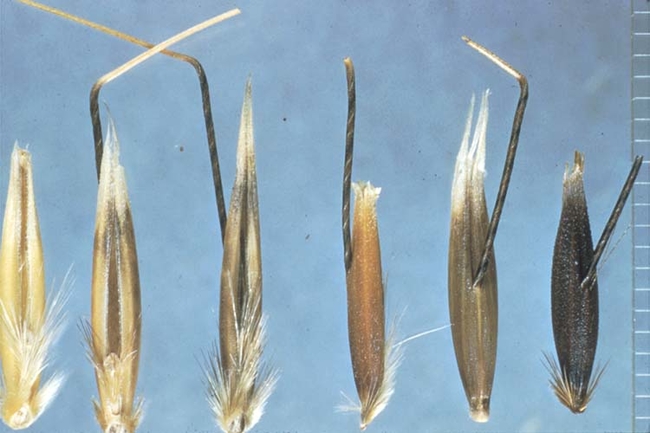
Spikelets: Have two large glumes (chaffy bracts) that enclose two to three seeds. Seeds (grains) are hairy toward the base with bent and twisted awns.
Panicum dichotomiflorum Michx.
Vegetative characteristics
-
Leaf blade: Seedlings have hairs on the lower leaf surfaces that disappear as the plant matures. Leaf blades of mature plants are hairless, often glossy-appearing and have a distinct white midvein.
-
Leaf sheath: Open, round, smooth and free of hairs.
-
Ligule: Fringe of hairs that’s 2 to 3 millimeters long.
-
Auricles: None.
-
Stems: Prominent nodes that are bent in different directions, giving the plant a zigzagged appearance.
Flowering characteristics
-
Inflorescence: Spreading panicle. Culms often have several panicles arising from lower-leaf sheaths. These frequently don’t fully extend from the boot.
-
Spikelets: Small with three apparent glumes; the first is short and blunt.
Panicum miliaceum L.
Vegetative characteristics
-
Leaf blade: Wide and with long hairs on both sides.
-
Leaf sheath: Open, round, prominently veined and coarsely hairy.
-
Ligule: Fringe of hairs.
-
Auricles: None
Flowering characteristics
-
Inflorescence: Spreading panicle that’s 6 to 12 inches wide.
-
Spikelets: Large (1/16 inch across) with three apparent chaffy glumes; the first is half-length and pointed at the tip. Seeds are olive-green to black and shiny.
Reviewed in 2024