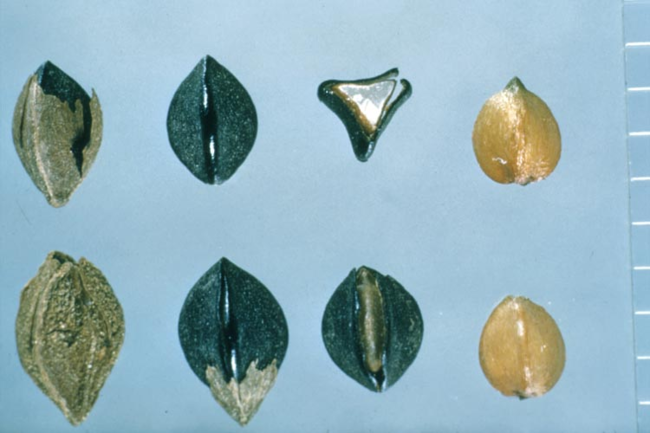
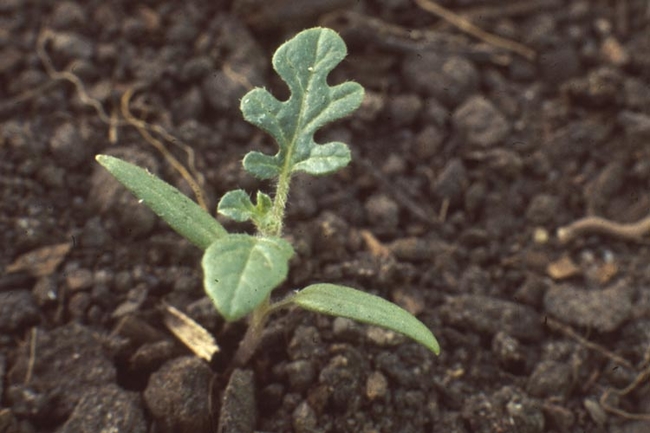
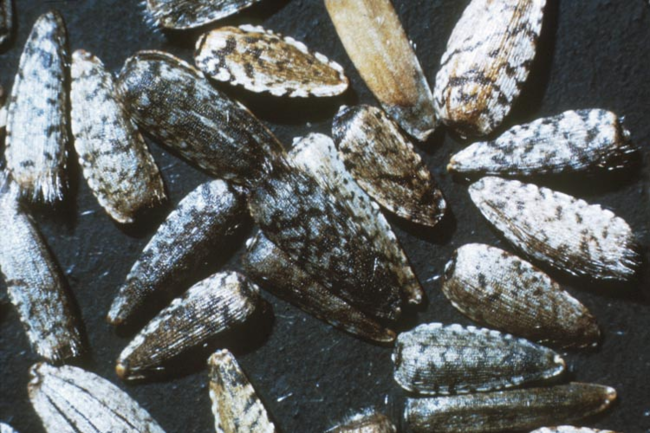
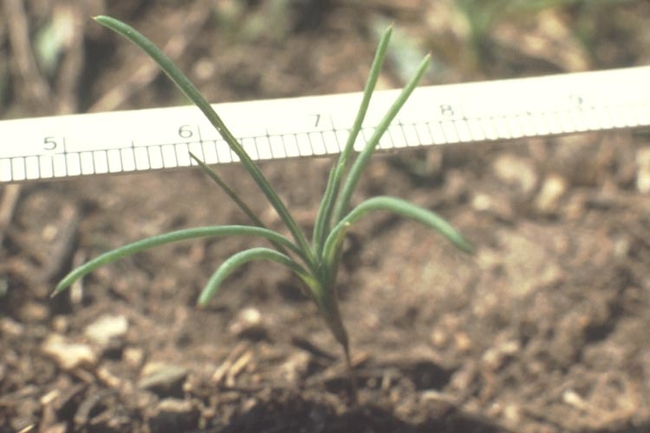
In this guide, you’ll find photos and identifying characteristics of the annual broadleaf weeds common to Minnesota.
Use these characteristics to help identify broadleaf weed seedlings.
Leaves
-
Broadleaf weed seedlings, in contrast to the grasses, usually have wider leaves with net-like venation.
-
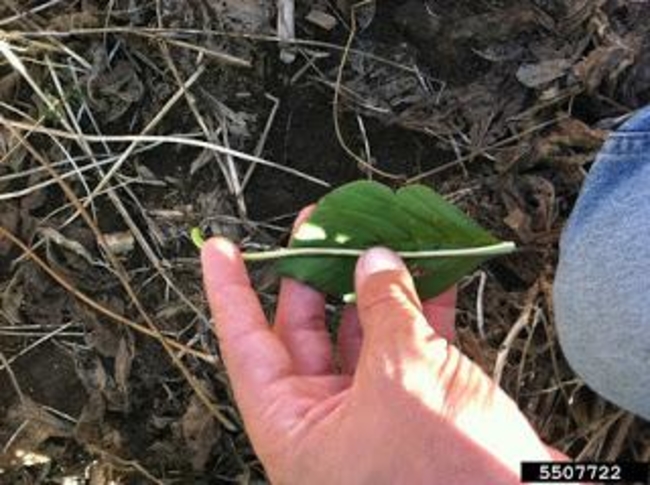
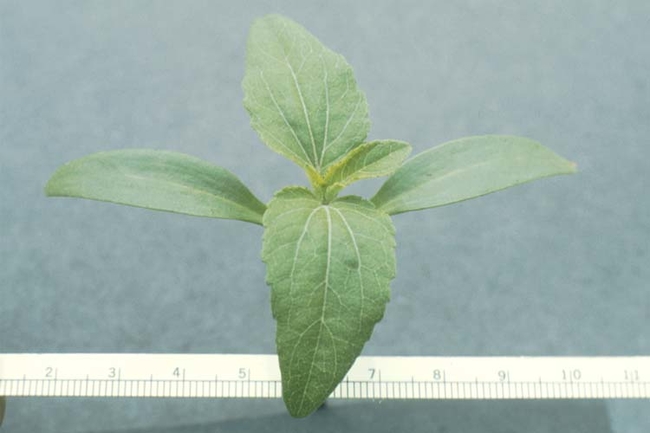
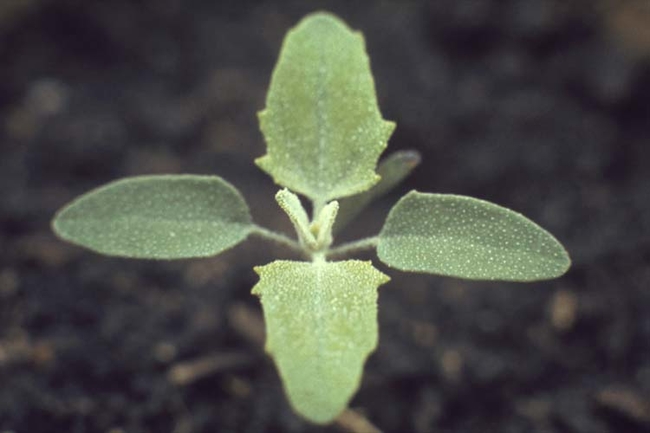
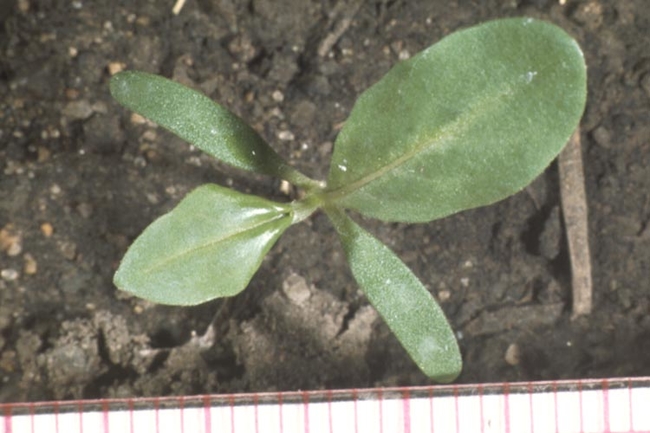
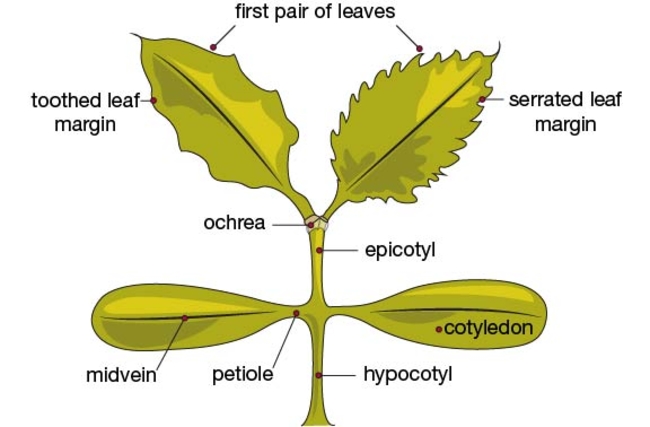
Broadleaves are dicots and have two cotyledons or seed-leaves. These usually emerge above the soil and expand to become the first visible “leaves.” The true leaves then develop above the cotyledons (Figure 1). However, in some broadleaf species, the cotyledon (seed) remains in the soil and the plumule (growing point and cluster of undeveloped true leaves) emerges above the soil line.
-
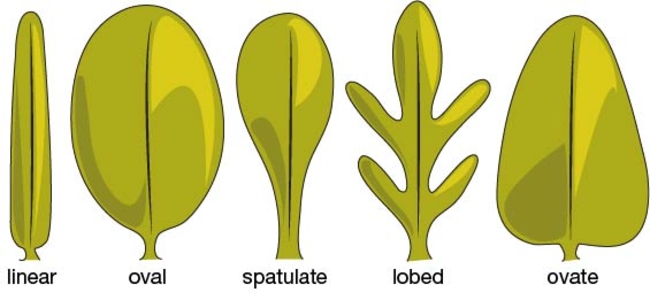
The shape and size of the cotyledons and first true leaves vary considerably among species (Figure 2).
-
Leaves may be alternate or opposite in arrangement on the stem. In some cases, the second leaf may appear so closely behind the first leaf that they appear to be opposite but later prove to be alternate.
-
The true leaves of broadleaf weeds usually have a petiole (leaf stalk). However, in some species, the true leaves may be sessile (without a leaf petiole).
-
Leaf petioles in the Buckwheat (Polygonaceae) plant family are encircled by a membranous sheath, called an ochrea.
Other plant characteristics
-
The stem below the cotyledons is called the hypocotyl. The stem above the cotyledon is the epicotyl.
-
Cotyledons are usually hairless but may be rough, while true leaves and plant stems may be hairy or smooth.
-
Seedlings may have an erect stem, be viny or twining in growth habit or be prostrate (growing flat on the ground).
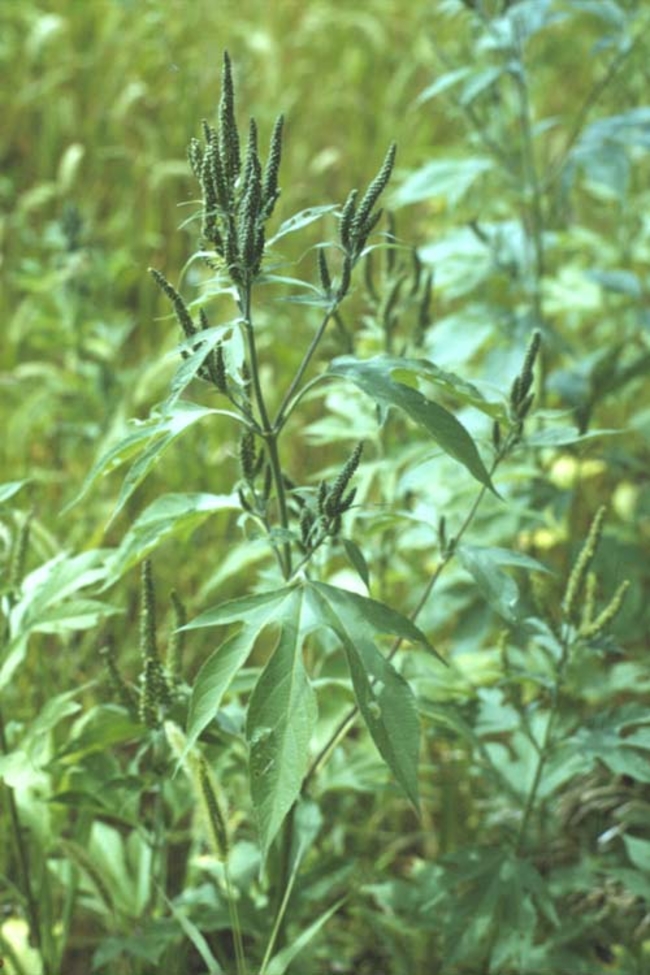
Waterhemp
Vegetative characteristics
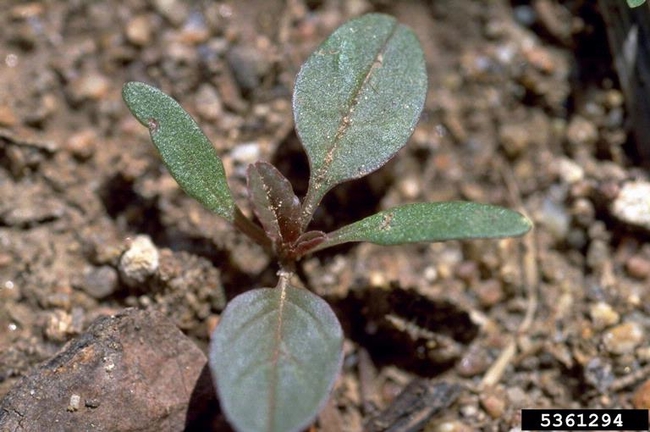
Cotyledons: Often more egg-shaped than other pigweed species.
Leaves: Long, narrow leaves. Smooth stems and leaves, unlike redroot pigweed.
Plant characteristics: Erect.
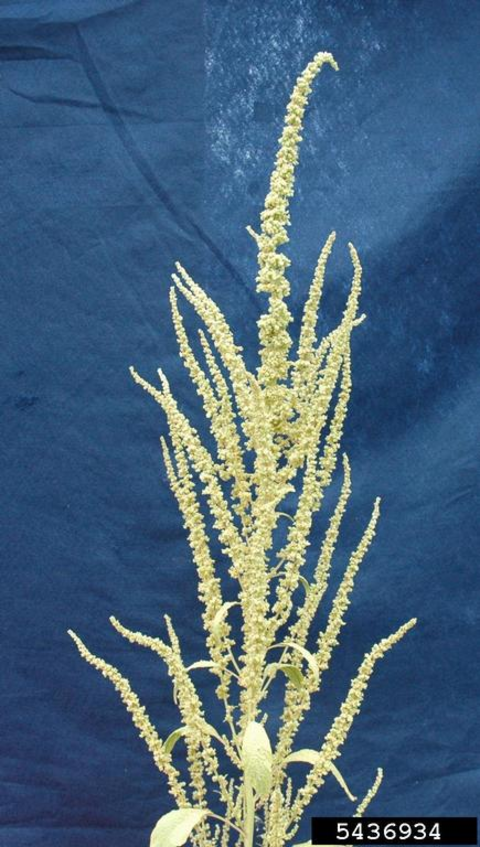
Flowering characteristics
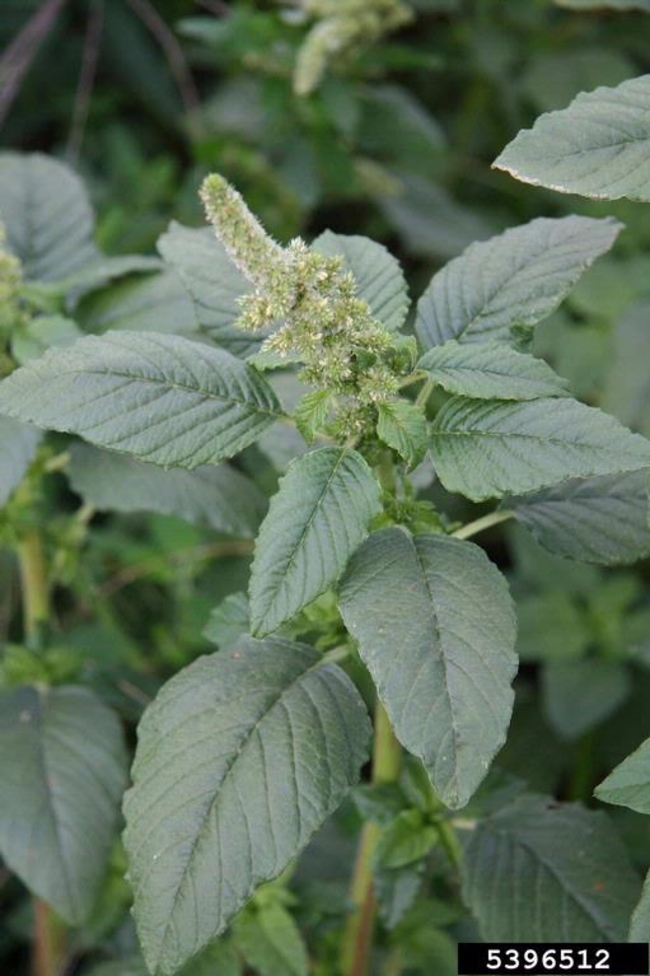
Leaves: Usually long and narrow. Smooth stems and leaves.
Flowers and seeds: Flowering structure near the top of the plant and at the tips of the branches. Either male or female.
Plant characteristics: Erect.
Palmer amaranth
Amaranthus palmeri
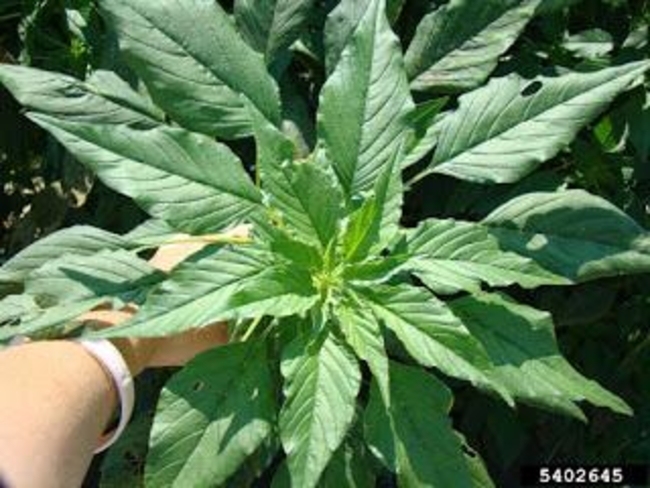
Vegetative characteristics
Cotyledons: Oval.
Leaves: Ovate- to diamond-shaped, giving it a poinsettia-like appearance. Smooth. May have a leaf tip hair. May also have a v-shaped watermark.
Petiole: As long or longer than the leaf.
Stem: Smooth, unlike redroot pigweed, which is hairy.
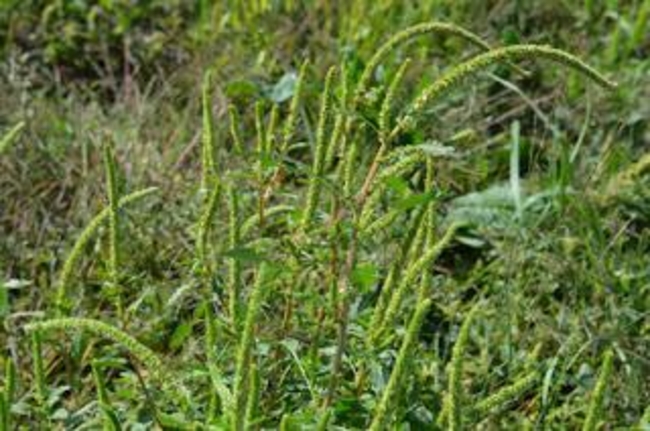
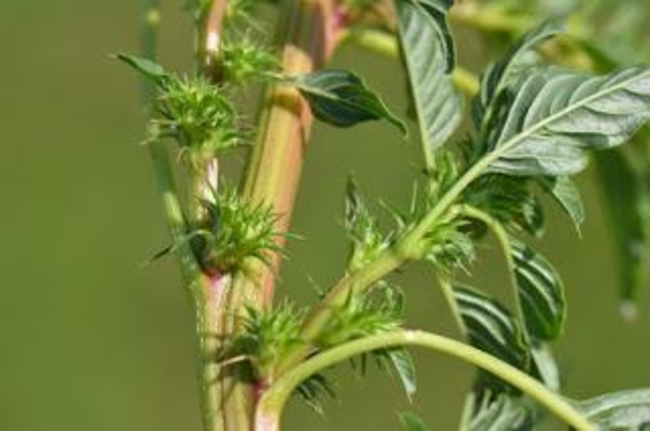
Flowering characteristics
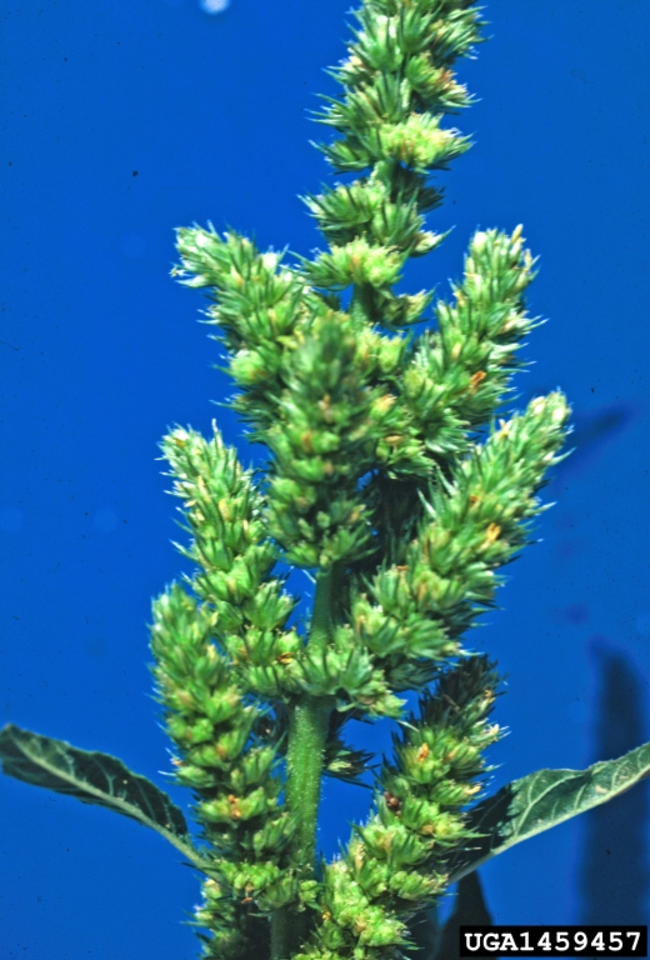
Reproduction: Plant is dioecious (male and female plants). Female inflorescences have sharp, spiny bracts. Male flowering structure is soft and sheds pollen.
Inflorescence: Main terminal seed head (inflorescence) is up to 3 feet long.
Seed production: Prolific seed producer. A single female plant can produce 100,000 to 500,000 seeds.
Plant characteristics
Height: Can reach 6 to 7 feet in unmown areas.
Overall: Plant is smooth with no hairs on stems and leaves, unlike redroot pigweed.
Additional guidance
Palmer amaranth in Minnesota: information from the Minnesota Department of Agriculture
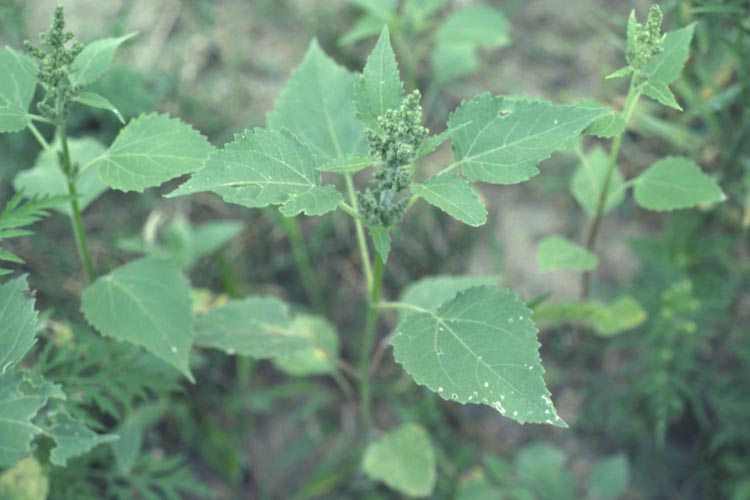
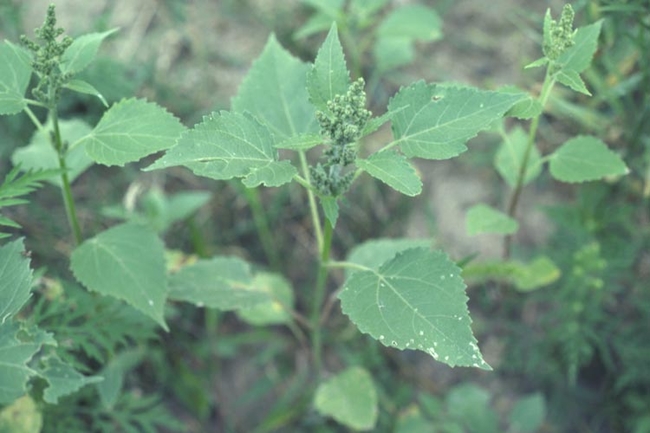
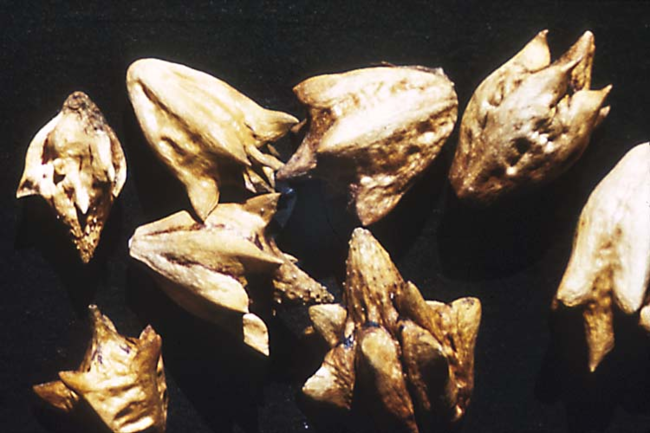
Redroot pigweed
Amaranthus retroflexis
Vegetative characteristics
Cotyledons: Linear with short petioles. Lower surface and midvein on upper surface are reddish.
Hypocotyl: Light red.
Leaves of seedling: Ovate and indented at the tip with a prominent midvein. Alternate leaf arrangement with purplish petioles.
Leaves of mature plant: Slightly toothed. Alternate leaf arrangement with a long petiole.
Flowering characteristics
Flowers: Small greenish flowers, subtended by bristles.
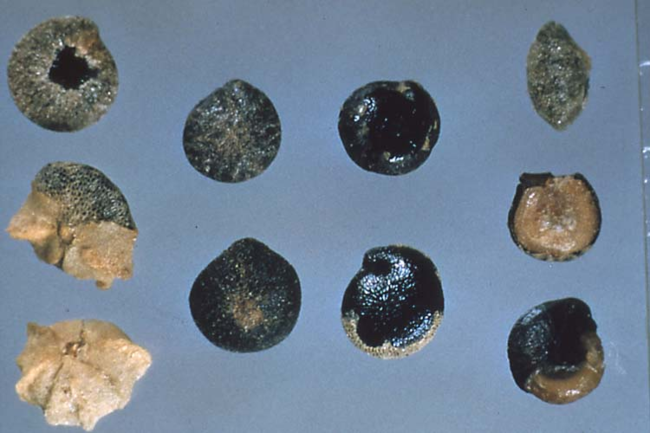
Seeds: Black and shiny.
Plant characteristics
Growth habit: Erect.
Pubescence: Very fine hairs throughout the plant, unlike tall waterhemp and Palmer amaranth.
Roots: Tap root is often reddish.
Vegetative characteristics
-
Cotyledons: Linear.
-
Hypocotyl: Short, reddish and often covered with short, bristle-like projections.
-
Leaves: Heart-shaped with entire (smooth) margins. Alternate leaf arrangement.
-
Petiole: Ochrea (sheath) present at the base of a long petiole.
Flowering characteristics
-
Flowers: Small and greenish.
-
Seeds: Triangular seeds.
Plant characteristics
-
Growth habit: Viny and twining.
Vegetative characteristics
-
Cotyledons: Linear.
-
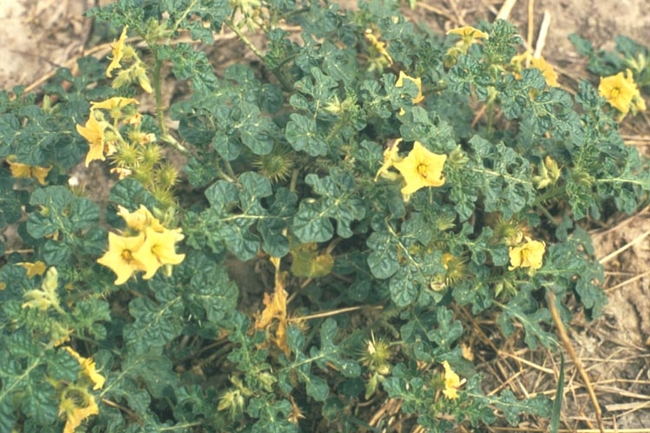
Leaves: Deeply lobed and alternate. Yellow spines develop on midrib and veins.
-
Petioles and stem: Prickly with yellow spines.
Flowering characteristics
-
Flowers: Yellow.
-
Seeds: Fruit a berry-like capsule with long, yellow spines.
Plant characteristics
- Growth habit: Erect or trailing.
Vegetative characteristics
-
Cotyledons: Long and linear, spread up to 80 millimeters. Tend to be triple-veined at the base with no petiole.
-
Hypocotyl: Rough and purplish.
-
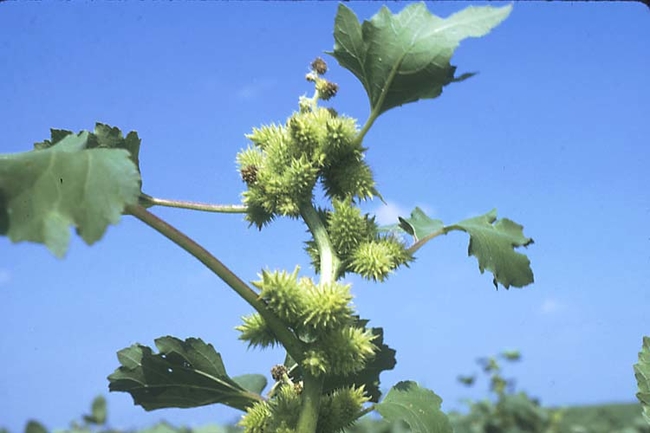
Leaves: Ovate and coarsely toothed or lobed with three prominent veins and a rough surface. Opposite leaf arrangement, then becoming alternate.
Flowering characteristics
-
Flowers and seeds: Greenish flowers.
-
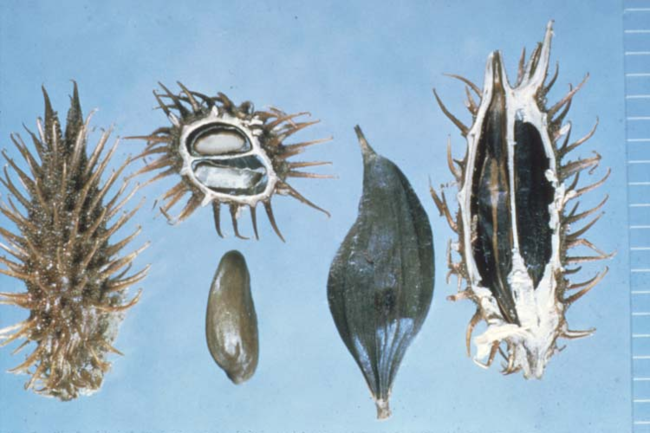
Seeds: Fruit is a spiny bur containing two seeds.
Plant characteristics
- Growth habit: Erect.
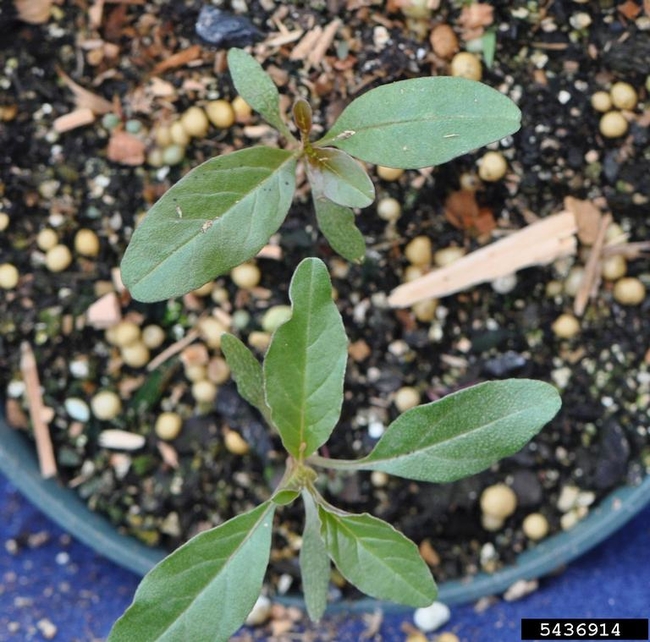
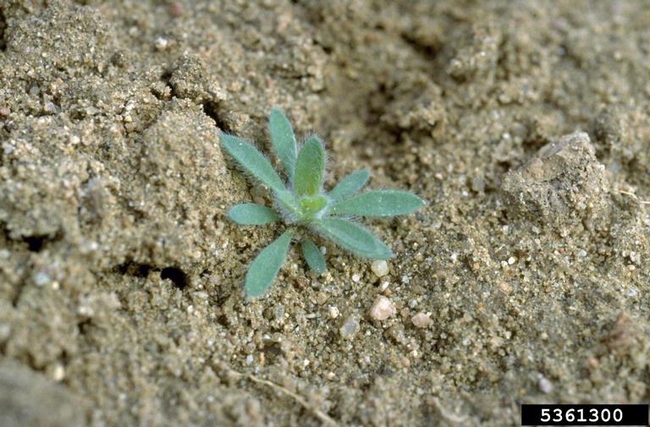
Vegetative characteristics
-
Cotyledons: Oval and very small, spreading about 11 millimeters. Gray or frosty-green on the upper surface, and red on the lower surface.
-
Hypocotyl: Reddish to purplish.
-
Leaves: Small, linear and densely hairy. First leaves are opposite, later alternate.
-
Stems: Often turn reddish in the fall.
Flowering characteristics
-
Flowers: Small and greenish.
-
Seeds: Small, one-seeded fruit.
Plant characteristics
- Growth habit: Erect and bushy.
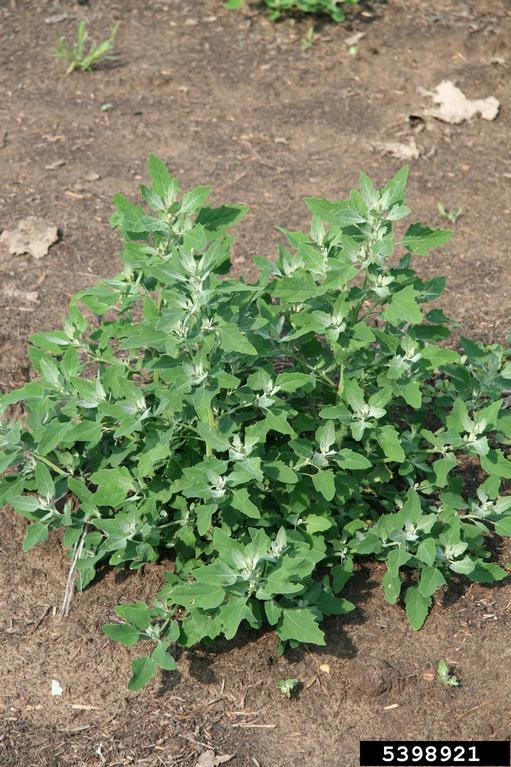
Vegetative characteristics
-
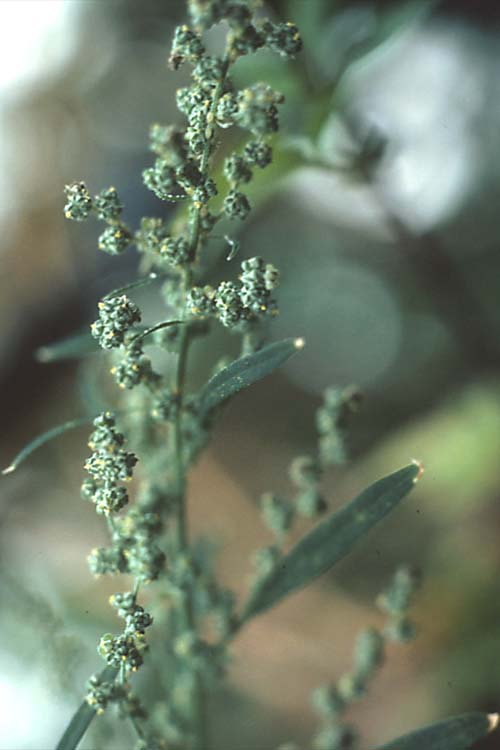
Cotyledons: Ovate with red on lower surface and light green on upper with a white, mealy appearance.
-
Hypocotyl: Light red.
-
Leaves: Slightly toothed with a white, mealy surface. Opposite leaf arrangement, then becoming alternate.
Flowering characteristics
-
Flowers and seeds: Gray-green flowers in small, round clusters.
-
Seeds: One-seeded fruit in a star-shaped hull. Hulled seed is small, black and round.
Plant characteristics
- Growth habit: Erect with many branches.
Vegetative characteristics
-
Cotyledons: Short and oval, with broad petioles and blunt tips.
-
Hypocotyl: Often turns reddish.
-
Leaves: Ovate, toothed leaves with a long petiole. Opposite leaf arrangement with bristly, hairy petioles and stems. Seedling leaves are also hairy.
Flowering characteristics
-
Flowers and seeds: Small, greenish-yellow flowers in clusters.
-
Seeds: One-seeded fruit.
Plant characteristics
- Growth habit: Erect.
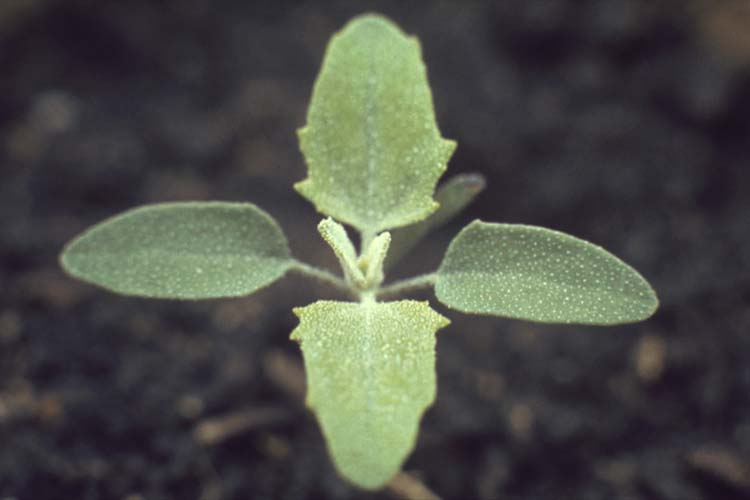
Vegetative characteristics
-
Cotyledons: Wider than long with a shallow, oval notch or indentation at the tip.
-
Hypocotyl: Usually reddish.
-
Leaves: Toothed or lobed, rough and hairy. Alternate leaf arrangement.
Flowering characteristics
-
Flowers: Yellow flowers with four petals.
-
Seeds: Fruit is a many-seeded cylindrical capsule with round seeds.
Plant characteristics
- Growth habit: Erect or trailing.
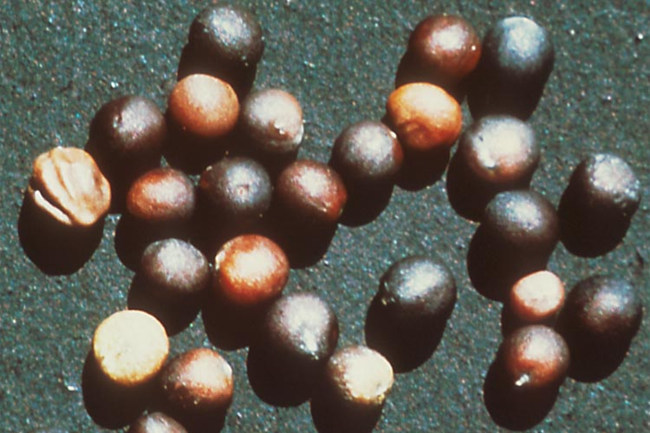
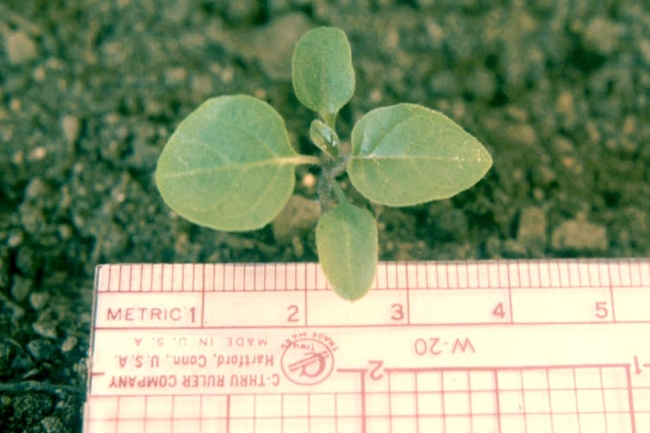
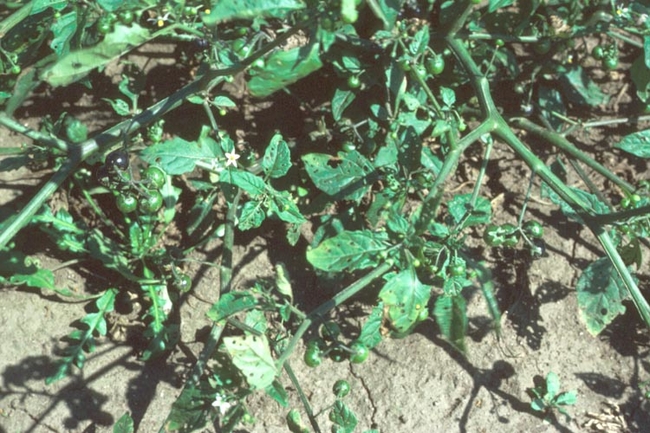
Vegetative characteristics
-
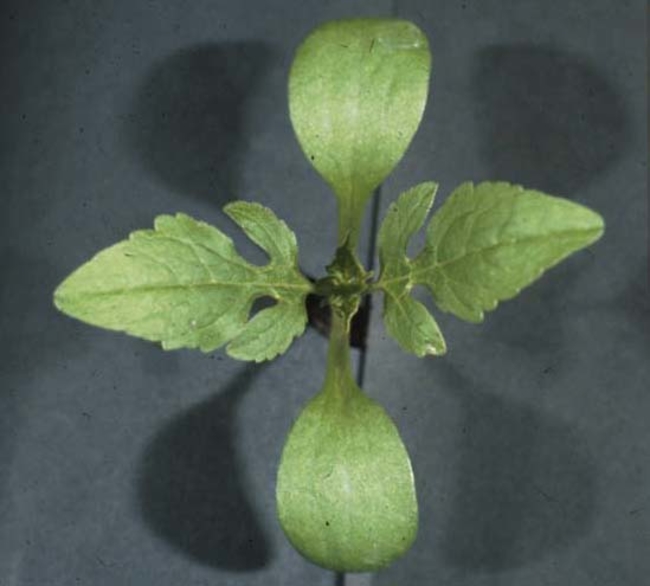
Cotyledons: Ovate.
-
Leaves of seedling: Ovate and dark green with prominent veins. Alternate leaf arrangement with purplish petioles.
-
Leaves of mature plant: Coarsely toothed, in an alternate leaf arrangement.
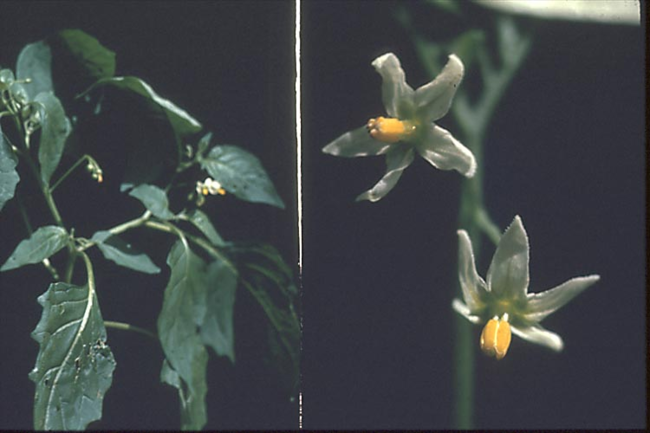
Flowering characteristics
-
Flowers and seeds: White to lavender flowers with yellow centers.
-
Seeds: Greenish berry fruit that turns black at maturity.
Plant characteristics
-
Growth habit: Erect or trailing.
Vegetative characteristics
-
Cotyledons: Linear to somewhat oval and thick. Veined at the base on lower surface. Thick and waxy.
-
Hypocotyl: Purple to dark green.
-
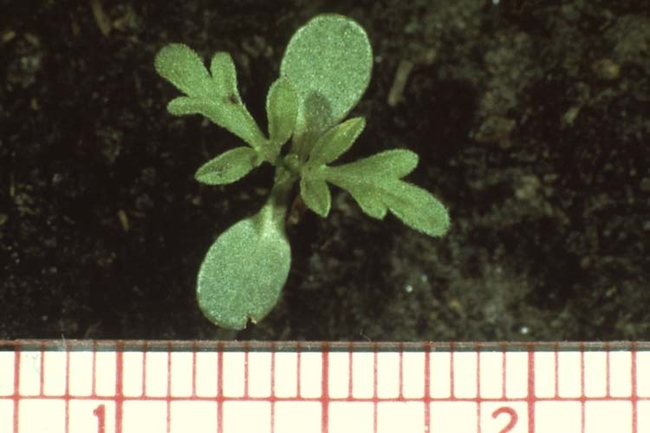
Leaves: Deeply lobed, becoming fern-like with dense, white hairs. Opposite leaf arrangement at the base of the plant, and an alternate arrangement above.
-
Stems: Densely hairy.
Flowering characteristics
-
Flowers and seeds: Small, yellowish-green flowers. Separate male and female flowers on the same plant.
-
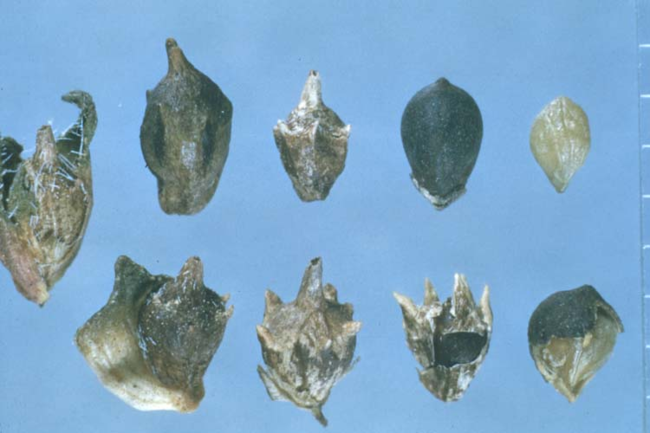
Seeds: Small, crown-shaped seeds.
Plant characteristics
- Growth habit: Erect.
Vegetative characteristics
-
Cotyledons: Large and broadly ovate. Thick and waxy.
-
Hypocotyl: Purple.
-
Leaves: Deeply three- to five-lobed and rough-surfaced. Opposite leaf arrangement, except at the top of the plant.
Flowering characteristics
-
Flowers: Small, greenish-yellow flowers. Separate male and female flowers on the same plant.
-
Seeds: Crown-shaped seeds that are 1/4 inch or more across.
Plant characteristics
- Growth habit: Erect.
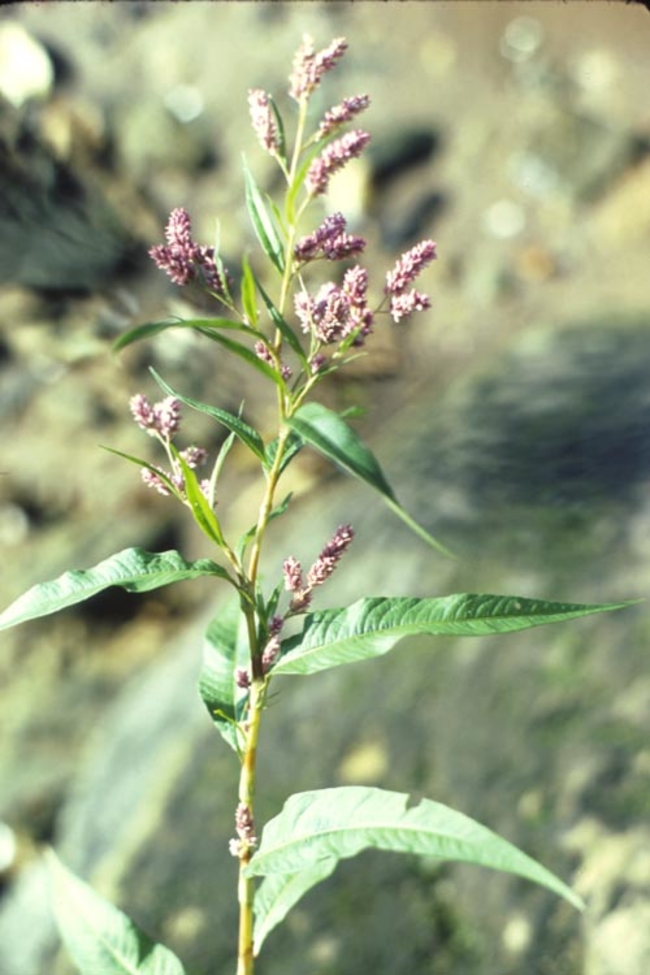
Vegetative characteristics
-
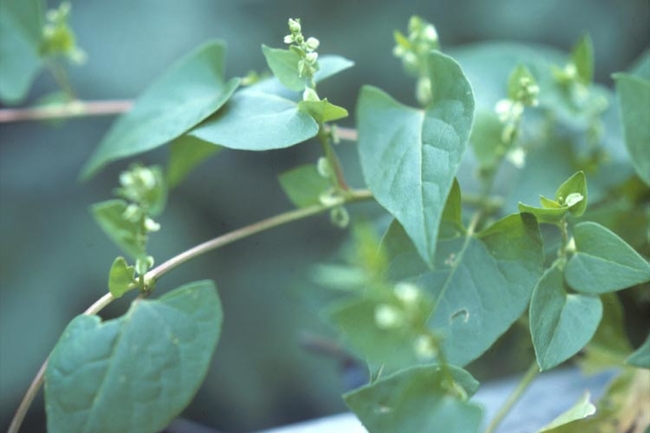
Cotyledons: Linear on one edge, curved on the other. Reddish blotch on the lower surface.
-
Hypocotyl: Reddish and smooth.
-
Leaves: Long, lanceolate shape with entire (smooth) leaf margins in an alternate leaf arrangement.
-
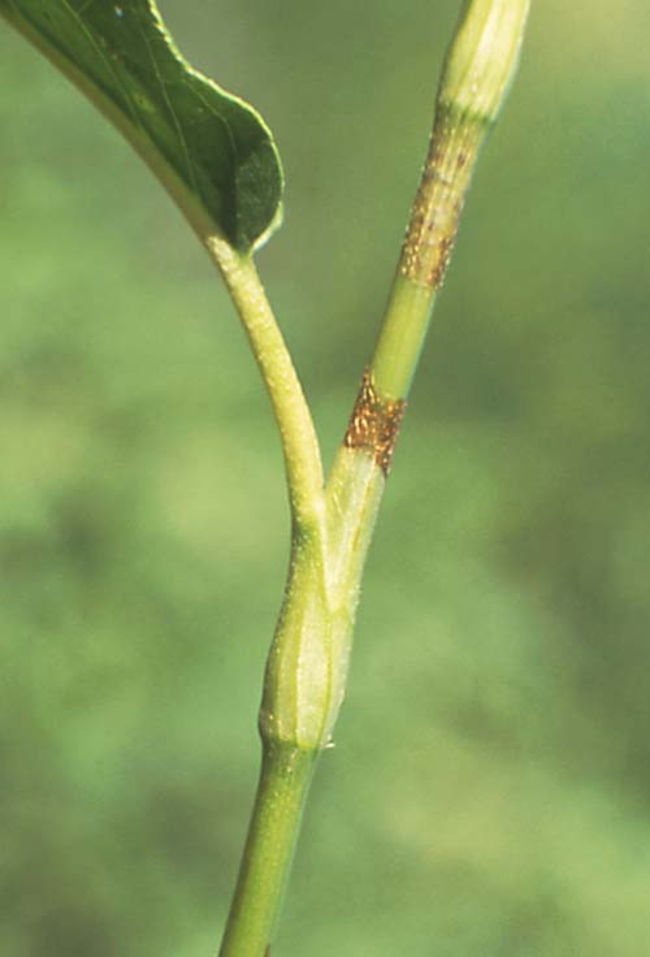
Petiole: Ochrea at the base of the short petiole. Ochrea lacks a fringe of hairs at the top, which helps distinguish it from other similar weeds.
-
Stems: Swollen stem nodes.
Flowering characteristics
-
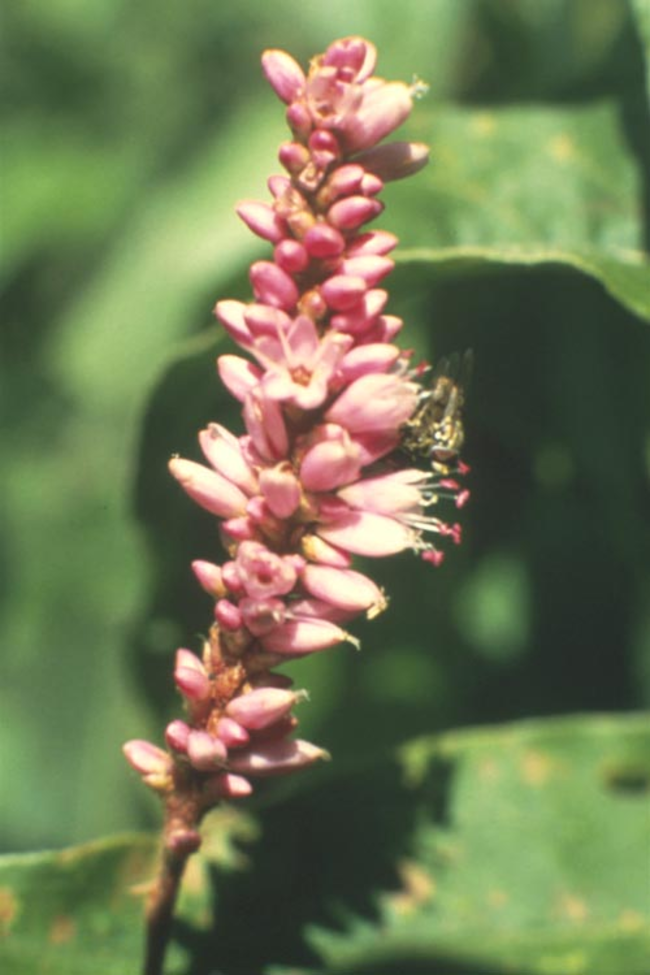
Flowers and seeds: Flowers in pink, raceme-like clusters.
-
Seeds: Shiny, lens-shaped seeds.
Plant characteristics
- Growth habit: Erect or trailing.
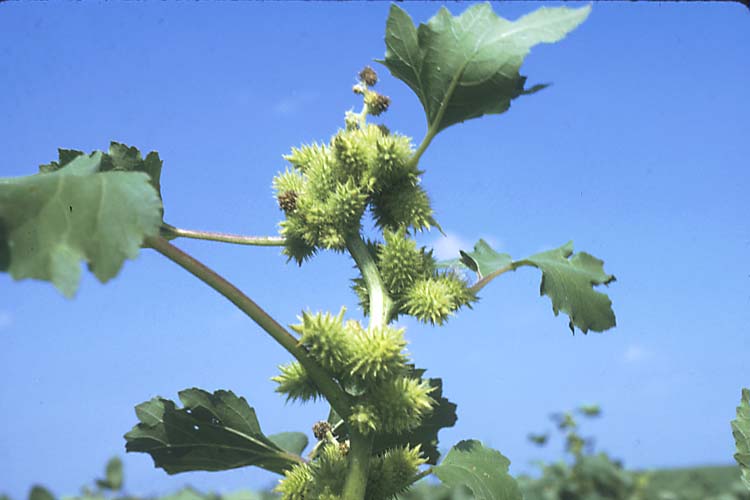
Vegetative characteristics
-
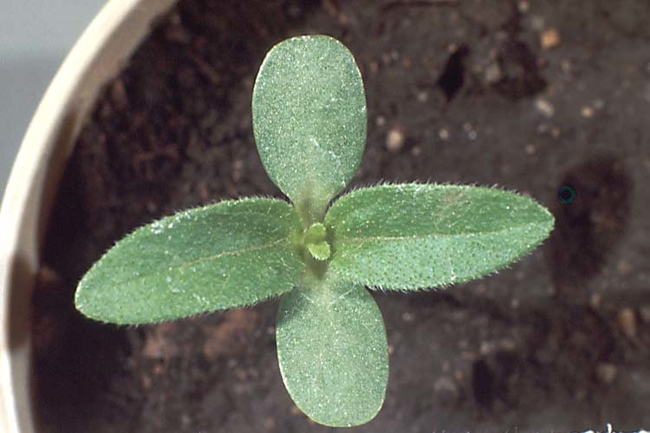
Cotyledons: Oval and rough.
-
Leaves: Coarsely toothed, rough and hairy. Opposite leaf arrangement at the base of the plant, and an alternate arrangement above.
-
Petiole: Long.
Flowering characteristics
-
Flowers and seeds: Yellow flowers in large heads with a dark center.
-
Seeds: Large, oblong seeds with many per head.
Plant characteristics
-
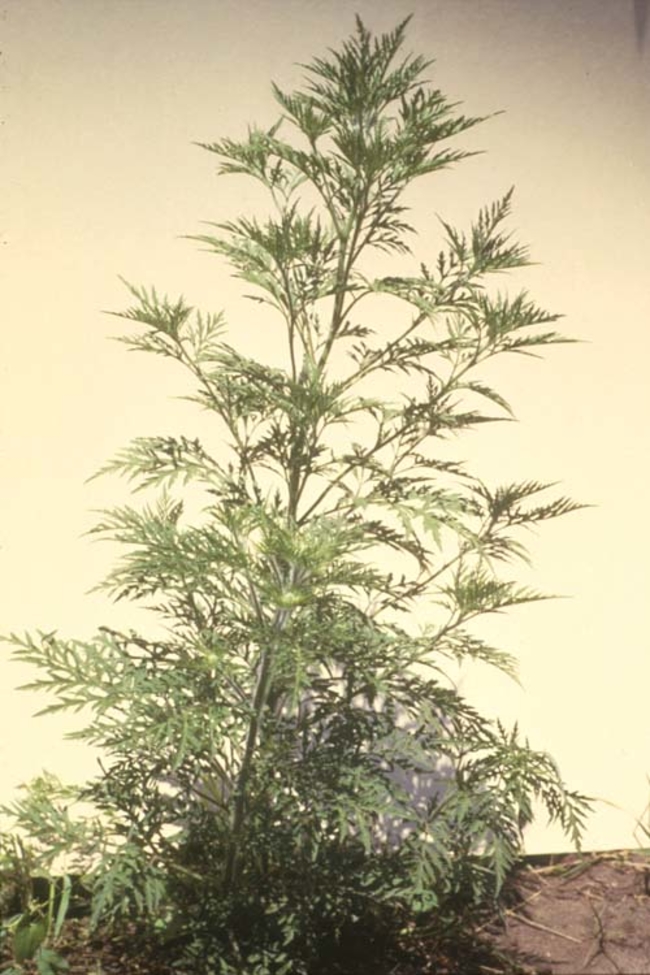
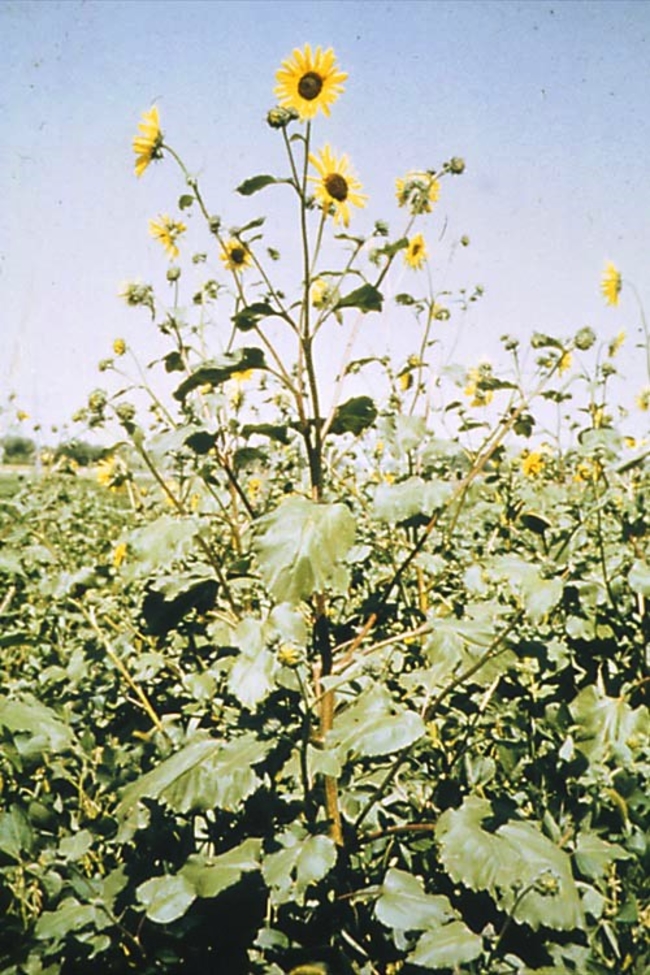
Growth habit: Erect and tall.
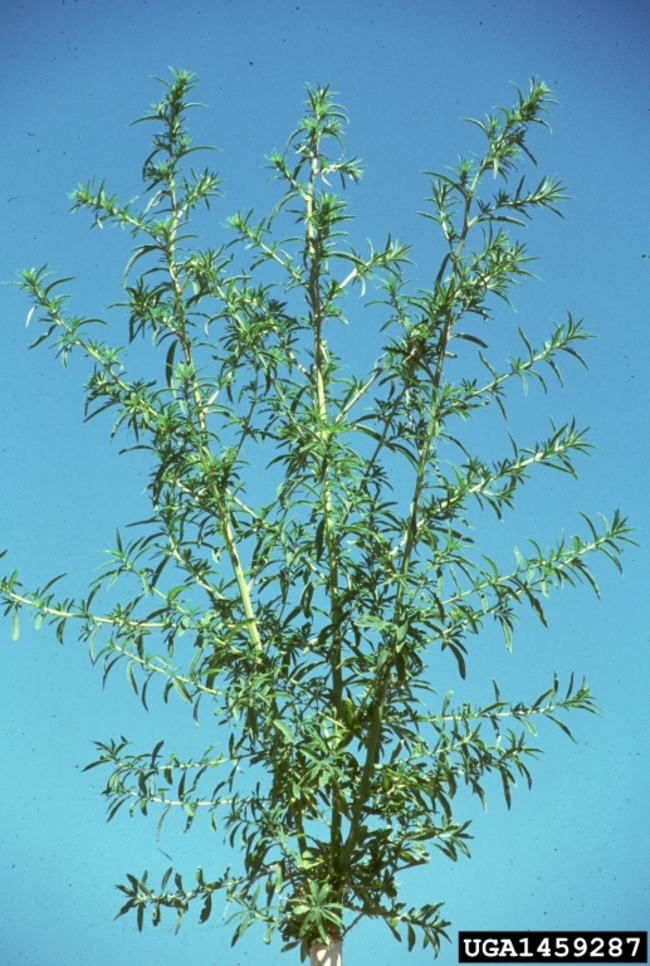
Vegetative characteristics
-
Cotyledons: Linear and thread-like with no petioles.
-
Hypocotyl: Reddish.
-
Leaves: Very narrow, thread-like and cylindrical. First leaves appear in an opposite arrangement, and later become alternate and spine-tipped.
-
Stems: Often streaked with red.
Flowering characteristics
-
Flowers and seeds: Small, grayish-green flowers.
-
Seeds: Coiled.
Plant characteristics
-
Growth habit: Erect.
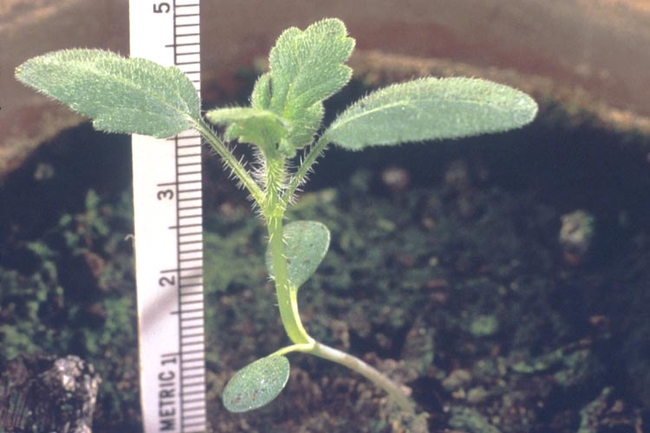
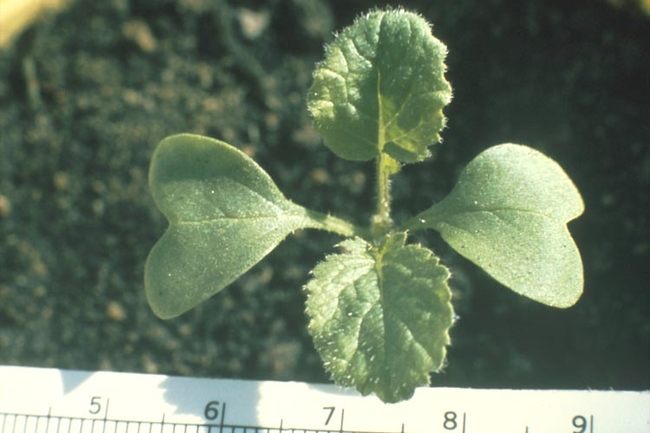
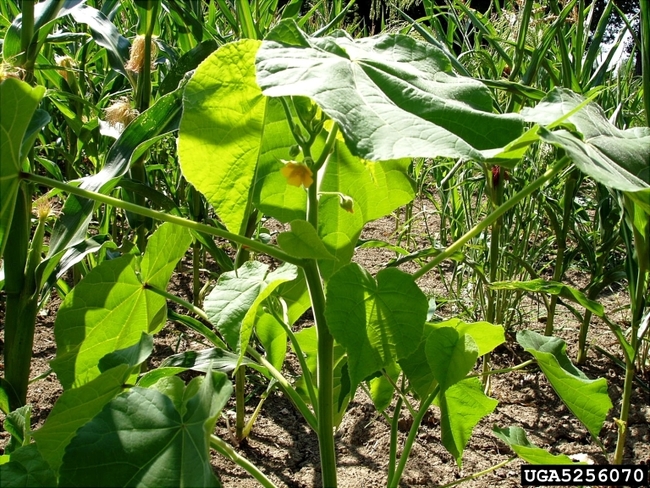
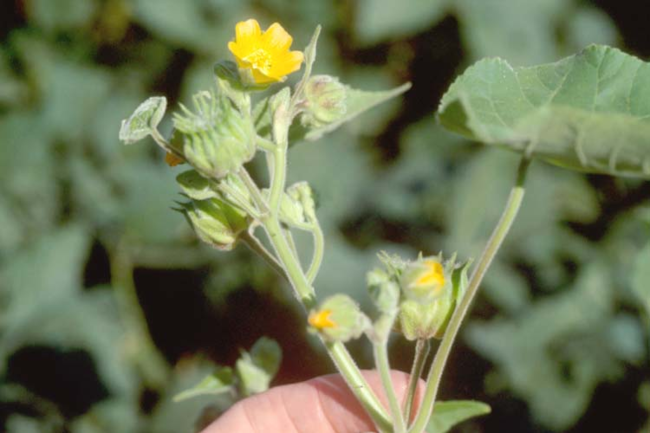
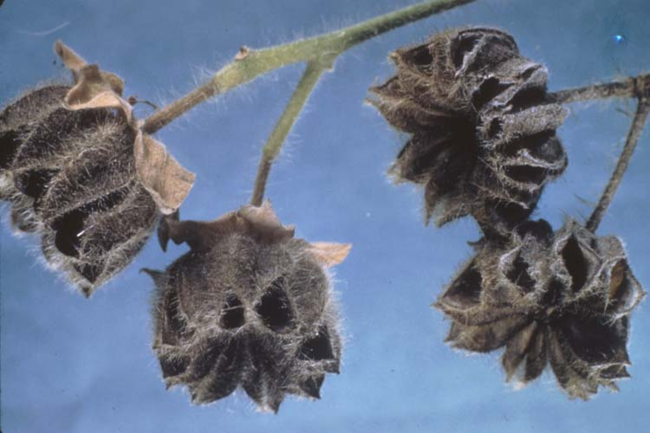
Vegetative characteristics
-
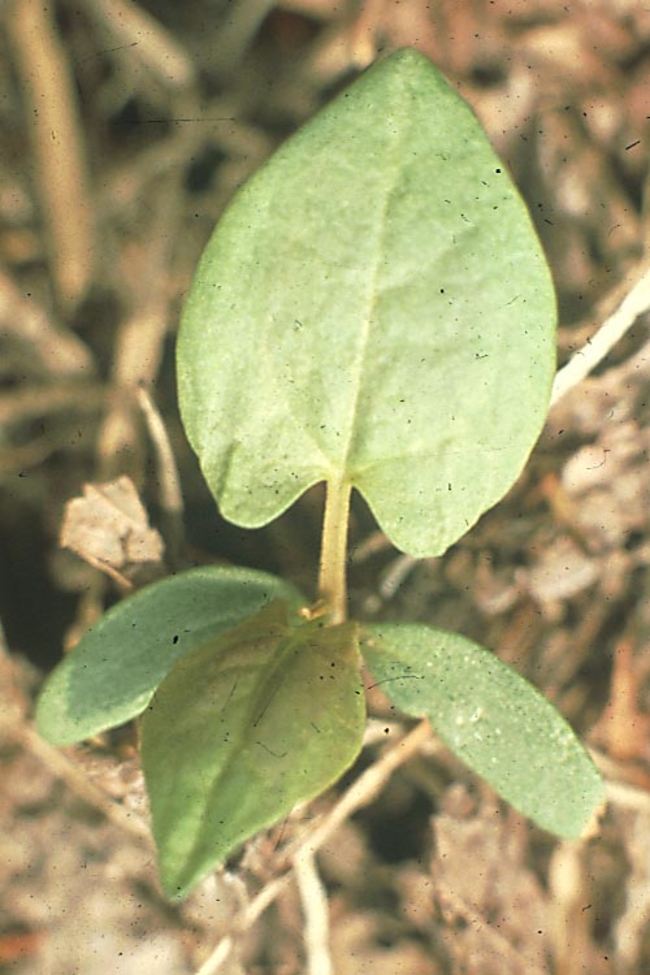
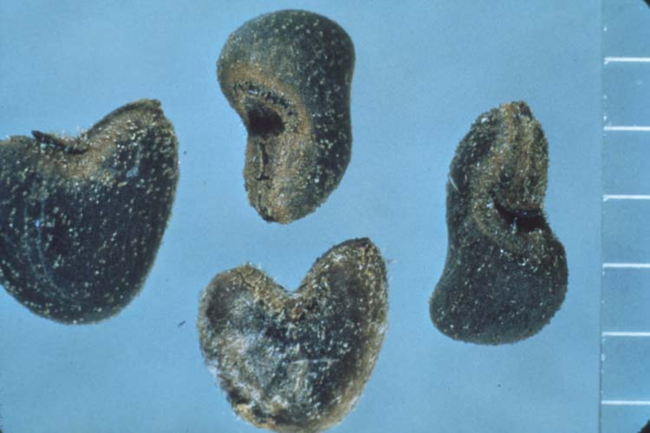
Cotyledons: Heart-shaped with blunt tips.
-
Leaves: Large, heart-shaped, velvety, soft and hairy. Alternate leaf arrangement.
-
Stems: Pubescent.
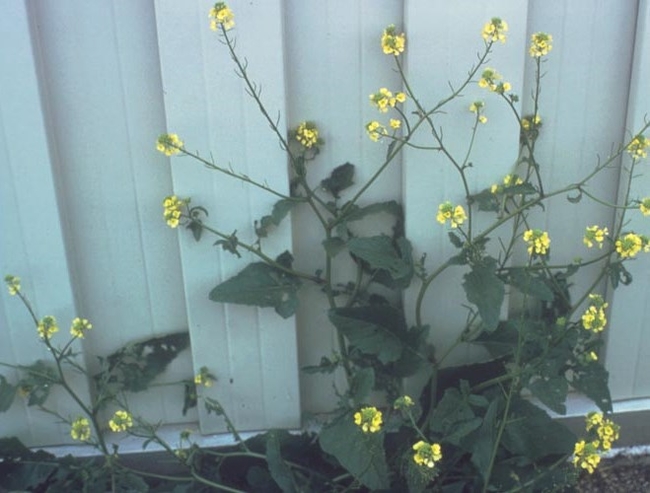
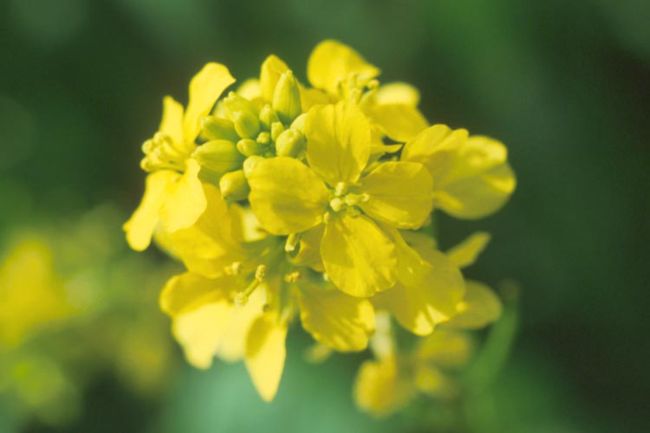
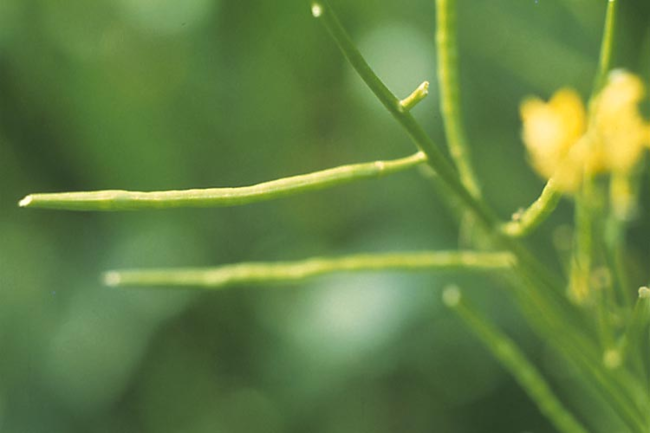
Flowering characteristics
-
Flowers: Large and yellow.
-
Seeds: Fruit is a button-like capsule with numerous heart-shaped seeds.
Plant characteristics
-
Growth habit: Erect with many branches and a strong odor.
Reviewed in 2022