Quick facts
- Roaring refers to a condition that greatly reduces a horse’s airflow during exercise.
- Partial blocking of the airway causes a “roar” sound, low tolerance for exercise and difficulty breathing after exercise.
- Surgery may improve the performance of roaring horses.
What is roaring?
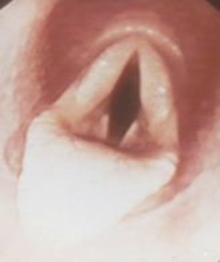
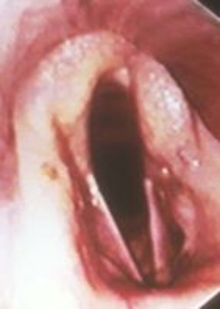
Roaring (laryngeal hemiplegia) is a condition in horses that greatly reduces their airflow during exercise. Affected horses make a “roar” sound under work. Damage or breakdown of the laryngeal nerve causes roaring.
The term laryngeal hemiplegia means paralysis of half of the larynx. The larynx closes when horses swallow food and opens to provide maximum airflow. Paralysis in the larynx reduces the amount of oxygen a horse can inhale during work. Usually, affected horses can’t tolerate exercise.
Roaring is more common in racehorses and other performance horses.
Signs of roaring
-
“Roar” or whistling noise heard during exercise.
-
Low and decreasing tolerance for exercise.
-
Difficulty breathing during or after exercise.
Diagnosis
Veterinarians may diagnose roaring by the following methods:
-
Standing or working endoscopy
-
Ultrasound
The severity of roaring is graded on a scale of 1 to 4, with 4 being the most severe.
Treatment
A tieback procedure (laryngoplasty) can restore the upper airway to a more normal size. In this procedure, surgeons tie back the paralyzed part of the larynx.
Often, veterinarians also remove small sacs in the larynx that also cause noise.
Recovery
Horses often remain in the hospital for 48 hours to receive antibiotics and pain relievers. An 8-week period of stall rest and walking follows this.
About 70 percent of racehorses have improved performance after surgery. Surgery may improve performance in over 70 percent of dressage horses.
Reviewed in 2021